Screening of Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting Gc Protein of RVFV
- PMID: 40285002
- PMCID: PMC12031069
- DOI: 10.3390/v17040559
Screening of Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting Gc Protein of RVFV
Abstract
Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV) is a mosquito-transmitted bunyavirus that can cause substantial morbidity and mortality in livestock and humans, for which there are no currently available licensed human therapeutics or vaccines. Therefore, the development of safe and effective antivirals is both necessary and urgent. The Gc protein is the primary target of the neutralizing antibody response related to Rift Valley fever virus. Here, we report one Gc-specific neutralizing antibody (NA137) isolated from an alpaca and one bispecific antibody (E2-NA137), the protective efficacies of which we evaluated in A129 mice. In this prophylactic study, the survival rates of the NA137 and E2-NA137 groups were both 80%, and in the treatment study, the survival rates were 20% and 60%, respectively. Altogether, our results emphasize that NA137 and E2-NA137 provide a potential approach for treating RVFV either prophylactically or therapeutically.
Keywords: Gc protein; Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV); VHH; bispecific antibody (bsAb); nanobody (Nb); neutralizing antibody (NAb).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
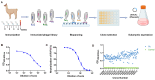

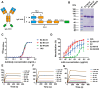
References
-
- Bird B.H., Githinji J.W., Macharia J.M., Kasiiti J.L., Muriithi R.M., Gacheru S.G., Musaa J.O., Towner J.S., Reeder S.A., Oliver J.B., et al. Multiple virus lineages sharing recent common ancestry were associated with a Large Rift Valley fever outbreak among livestock in Kenya during 2006–2007. J. Virol. 2008;82:11152–11166. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01519-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

