Investigation of Ultrasound Transmit-Receive Sequence That Enables Both High-Frame-Rate Vascular Wall Velocity Estimation and High-Contrast B-Mode Images
- PMID: 40285129
- PMCID: PMC12031348
- DOI: 10.3390/s25082441
Investigation of Ultrasound Transmit-Receive Sequence That Enables Both High-Frame-Rate Vascular Wall Velocity Estimation and High-Contrast B-Mode Images
Abstract
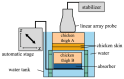
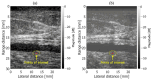
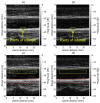
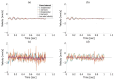
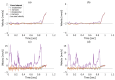
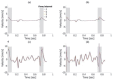
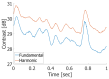
In this study, we designed an ultrasound transmit-receive sequence to achieve high-frame-rate vascular wall velocity estimation and high-contrast B-mode imaging. The proposed sequence extends conventional dual-transmission schemes by incorporating a third transmission with 180° phase inversion, enabling harmonic imaging via the pulse inversion (PI) method. To mitigate the frame rate reduction caused by the additional transmission, the number of simultaneously transmitted focused beams was increased from two to four, resulting in a frame rate of 231 Hz. A two-dimensional phase-sensitive motion estimator was employed for motion estimation. In vitro experiments using a chicken thigh moving in two dimensions yielded RMSE values of 3% (vertical) and 16% (horizontal). In vivo experiments on a human carotid artery demonstrated that the PI method achieved a lumen-to-tissue contrast improvement of 0.96 dB and reduced artifacts. Velocity estimation of the posterior vascular wall showed generally robust performance. These findings suggest that the proposed method has strong potential to improve atherosclerosis diagnostics by combining artifact-suppressed imaging with accurate motion analysis.
Keywords: multi-line transmission; phase-sensitive motion estimator; pulse inversion; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Yamasaki Y., Kodama M., Nishizawa H., Sakamoto K., Matsuhisa M., Kajimoto Y., Kosugi K., Shimizu Y., Kawamori R., Hori M. Carotid intima-media thickness in Japanese type 2 diabetic subjects: Predictors of progression and relationship with incident coronary heart disease. Diab. Care. 2000;23:1310–1315. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.9.1310. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

