Recent Advances in MOF-Based Materials for Biosensing Applications
- PMID: 40285162
- PMCID: PMC12031313
- DOI: 10.3390/s25082473
Recent Advances in MOF-Based Materials for Biosensing Applications
Abstract
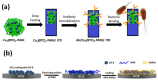
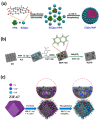
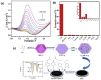
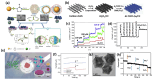
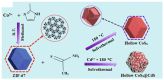
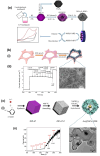
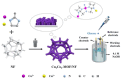
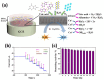
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) or coordination polymers have gained enormous interest in recent years due to their extraordinary properties, including their high surface area, tunable pore size, and ability to form nanocomposites with various functional materials. MOF materials possess redox-active properties that are beneficial for electrochemical sensing applications. Furthermore, the tunable pore size and high surface area improve the adsorption or immobilization of enzymes, which can enhance the sensitivity and selectivity for specific analytes. Additionally, MOF-derived metal sulfides, phosphides, and nitrides demonstrate superior electrical conductivity and structural stability, ideal for electrochemical sensing. Moreover, the functionalization of MOFs further increases sensitivity by enhancing electrode-analyte interactions. The inclusion of carbon materials within MOFs enhances their electrical conductivity and reduces background current through optimized loading, preventing agglomeration and ensuring uniform distribution. Noble metals immobilized on MOFs offer improved stability and catalytic performance, providing larger surface areas and uniform nanoparticle dispersion. This review focuses on recent developments in MOF-based biosensors specifically for glucose, dopamine, H2O2, ascorbic acid, and uric acid sensing.
Keywords: MOF-derived carbon composites; MOF-derived metal oxides; MOF–noble metal composite; biosensing; metal–organic frameworks; phosphides; sulfides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

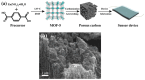
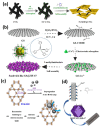
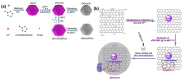
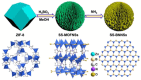


References
-
- Zhou H.C., Long J.R., Yaghi O.M. Introduction to Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012;112:673–674. - PubMed
-
- Li H., Eddaoudi M., O’Keeffe M., Yaghi O.M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature. 1999;402:276–279. doi: 10.1038/46248. - DOI
-
- Stock N., Biswas S. Synthesis of Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Routes to Various MOF Topologies, Morphologies, and Composites. Chem. Rev. 2012;112:933–969. - PubMed
-
- Horcajada P., Gref R., Baati T., Allan P.K., Maurin G., Couvreur P., Férey G., Morris R.E., Serre C. Metal–Organic Frameworks in Biomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2012;112:1232–1268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

