Boosting Skin Cancer Classification: A Multi-Scale Attention and Ensemble Approach with Vision Transformers
- PMID: 40285168
- PMCID: PMC12030980
- DOI: 10.3390/s25082479
Boosting Skin Cancer Classification: A Multi-Scale Attention and Ensemble Approach with Vision Transformers
Abstract
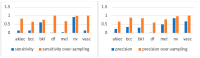
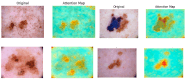
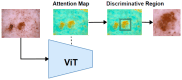
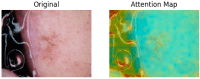
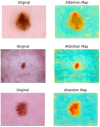
Skin cancer is a significant global health concern, with melanoma being the most dangerous form, responsible for the majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Early detection of skin cancer is critical, as it can drastically improve survival rates. While deep learning models have achieved impressive results in skin cancer classification, there remain challenges in accurately distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions. In this study, we introduce a novel multi-scale attention-based performance booster inspired by the Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture, which enhances the accuracy of both ViT and convolutional neural network (CNN) models. By leveraging attention maps to identify discriminative regions within skin lesion images, our method improves the models' focus on diagnostically relevant areas. Additionally, we employ ensemble learning techniques to combine the outputs of several deep learning models using majority voting. Our skin cancer classifier, consisting of ViT and EfficientNet models, achieved a classification accuracy of 95.05% on the ISIC2018 dataset, outperforming individual models. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating attention-based multi-scale learning and ensemble methods in skin cancer classification.
Keywords: deep learning; image processing; neural networks; skin cancer classification; transformer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SkinEHDLF a hybrid deep learning approach for accurate skin cancer classification in complex systems.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 28;15(1):14913. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98205-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40295588 Free PMC article.
-
A robust deep learning framework for multiclass skin cancer classification.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 10;15(1):4938. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89230-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39930026 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Skin lesion prediction and classification technique: ViT-GradCAM.Skin Res Technol. 2024 Sep;30(9):e70040. doi: 10.1111/srt.70040. Skin Res Technol. 2024. Retraction in: Skin Res Technol. 2024 Nov;30(11):e70154. doi: 10.1111/srt.70154. PMID: 39221858 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Skin cancer classification via convolutional neural networks: systematic review of studies involving human experts.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Oct;156:202-216. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.06.049. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34509059
-
Decoding skin cancer classification: perspectives, insights, and advances through researchers' lens.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 18;14(1):30542. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81961-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39695157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Australian Bureau of Statistics . Causes of Death. ABS; Canberra, Australia: 2019. [(accessed on 1 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/health/causes-death/causes-death-austr....
-
- Street W. Cancer Facts & Figures. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2019. [(accessed on 1 November 2022)]. Available online: http://cancerstatisticscenter.cancer.org.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

