Reliable ECG Anomaly Detection on Edge Devices for Internet of Medical Things Applications
- PMID: 40285186
- PMCID: PMC12031393
- DOI: 10.3390/s25082496
Reliable ECG Anomaly Detection on Edge Devices for Internet of Medical Things Applications
Abstract
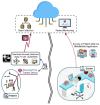
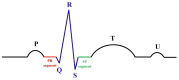
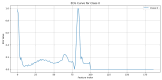
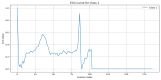
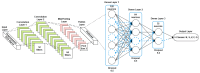
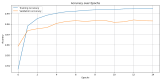
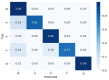
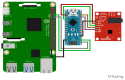
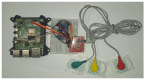
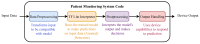
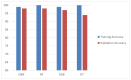
The advent of Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML) has unlocked the potential to deploy machine learning models on resource-constrained edge devices, revolutionizing real-time monitoring in Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) applications. This study introduces a novel approach to real-time electrocardiogram (ECG) anomaly detection by integrating TinyML with edge Artificial Intelligence (AI) on low-power embedded systems. We demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of deploying optimized models on edge devices, such as the Raspberry Pi and Arduino, to detect ECG anomalies, including arrhythmias. The proposed workflow encompasses data preprocessing, feature extraction, and model inference, all executed directly on the edge device, eliminating the need for cloud resources. To address the constraints of memory and power consumption in wearable devices, we applied advanced optimization techniques, including model pruning and quantization, achieving an optimal balance between accuracy and resource utilization. The optimized model achieved an accuracy of 92.3% while reducing the power consumption to 0.024 mW, enabling continuous, long-term health monitoring with minimal energy requirements. This work highlights the potential of TinyML to advance edge AI for real-time medical applications.
Keywords: ECG; IoMT; TinyML; anomaly detection; edge AI; embedded systems; low-power.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
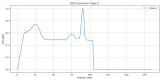
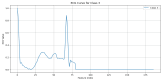
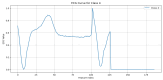
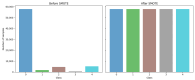

Similar articles
-
TinyML and edge intelligence applications in cardiovascular disease: A survey.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Mar;186:109653. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.109653. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39798504 Review.
-
Energy-efficient dynamic sensor time series classification for edge health devices.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024 Sep;254:108268. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2024.108268. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38870733
-
Tiny Machine Learning and On-Device Inference: A Survey of Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions.Sensors (Basel). 2025 May 19;25(10):3191. doi: 10.3390/s25103191. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ECG Biometric Authentication Using Self-Supervised Learning for IoT Edge Sensors.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2024 Nov;28(11):6606-6618. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2024.3455803. Epub 2024 Nov 6. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2024. PMID: 39250357
-
TinyML: Enabling of Inference Deep Learning Models on Ultra-Low-Power IoT Edge Devices for AI Applications.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 May 29;13(6):851. doi: 10.3390/mi13060851. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35744466 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence and ECG: A New Frontier in Cardiac Diagnostics and Prevention.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 9;13(7):1685. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071685. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Quincozes V.E., Quincozes S.E., Kazienko J.F., Gama S., Cheikhrouhou O., Koubaa A. A survey on IoT application layer protocols, security challenges, and the role of explainable AI in IoT (XAIoT) Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2024;23:1975–2002. doi: 10.1007/s10207-024-00828-w. - DOI
-
- Abadade Y., Temouden A., Bamoumen H., Benamar N., Chtouki Y., Hafid A.S. A Comprehensive Survey on TinyML. IEEE Access. 2023;11:96892–96922. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3294111. - DOI
-
- Allam A.H., Gomaa I., Zayed H.H., Taha M. IoT-based eHealth using blockchain technology: A survey. Clust. Comput. 2024;27:7083–7110. doi: 10.1007/s10586-024-04357-y. - DOI
-
- Paraschiv E.-A., Tudora E., Tîrziu E., Alexandru A. IoT & Cloud Computing-based Remote Healthcare Monitoring System for an Elderly-Centered Care; In Proceeding of the 2021 International Conference on e-Health and Bioengineering (EHB); Iasi, Romania. 18–19 April 2021; pp. 1–4. - DOI
-
- Zou R., Hung C.-L., Lo C.L., Yang C., Zhang W. Evaluation of the accuracy of ECG captured by CardioChip through comparison of ECG recording to a standard 12-lead ECG recording device; In Proceeding of the 2016 IEEE 25th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE); Santa Clara, CA, USA. 8–10 June 2016; pp. 1094–1098. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

