Copper Nanoclusters Anchored on Crumpled N-Doped MXene for Ultra-Sensitive Electrochemical Sensing
- PMID: 40285194
- PMCID: PMC12031129
- DOI: 10.3390/s25082508
Copper Nanoclusters Anchored on Crumpled N-Doped MXene for Ultra-Sensitive Electrochemical Sensing
Abstract
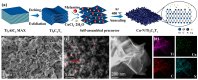
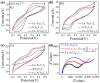
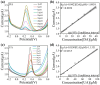
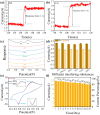
Simultaneous detection of dopamine (DA) and uric acid (UA) is essential for diagnosing neurological and metabolic diseases but hindered by overlapping electrochemical signals. We present an ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor using copper nanoclusters anchored on nitrogen-doped crumpled Ti3C2Tx MXene (Cu-N/Ti3C2Tx). The engineered 3D crumpled architecture prevents MXene restacking, exposes active sites, and enhances ion transport, while Cu nanoclusters boost electrocatalytic activity via accelerated electron transfer. Structural analyses confirm uniform Cu dispersion (3.0 wt%), Ti-N bonding, and strain-induced wrinkles, synergistically improving conductivity. The sensor achieves exceptional sensitivity (1958.3 and 1152.7 μA·mM-1·cm-2 for DA/UA), ultralow detection limits (0.058 and 0.099 μM for DA/UA), rapid response (<1.5 s), and interference resistance (e.g., ascorbic acid). Differential pulse voltammetry enables independent linear detection ranges (DA: 2-60 μM; UA: 5-100 μM) in biofluids, with 94.4% stability retention over 7 days. The designed sensor exhibits excellent capabilities for DA and UA detection. This work provides a novel design strategy for developing high-performance electrochemical sensors.
Keywords: Cu nanoclusters; MXene; crumpled structure; dopamine; uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sriram B., Kogularasu S., Wang S.-F., Sheu J.-K. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Mediated Synthesis of Spinel Zinc Chromite Nanoparticles: A Simple Label-Free Electrochemical Sensor for Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023;6:17593–17602. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c02775. - DOI
-
- Shukla R.P., Aroosh M., Matzafi A., Ben-Yoav H. Partially Functional Electrode Modifications for Rapid Detection of Dopamine in Urine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2004146. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202004146. - DOI
-
- Shi Z., Wu X., Zou Z., Yu L., Hu F., Li Y., Guo C., Li C.M. Screen-Printed Analytical Strip Constructed with Bacteria-Templated Porous N-Doped Carbon Nanorods/Au Nanoparticles for Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine Molecules. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021;186:113303. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113303. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feng J., Li Q., Cai J., Yang T., Chen J., Hou X. Electrochemical Detection Mechanism of Dopamine and Uric Acid on Titanium Nitride-Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite with and without Ascorbic Acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019;298:126872. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.126872. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

