A Review of Vision-Based Multi-Task Perception Research Methods for Autonomous Vehicles
- PMID: 40285295
- PMCID: PMC12030850
- DOI: 10.3390/s25082611
A Review of Vision-Based Multi-Task Perception Research Methods for Autonomous Vehicles
Abstract
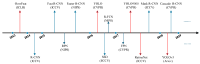
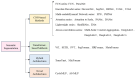
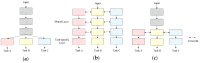
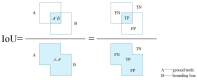
Multi-task perception technology for autonomous driving significantly improves the ability of autonomous vehicles to understand complex traffic environments by integrating multiple perception tasks, such as traffic object detection, drivable area segmentation, and lane detection. The collaborative processing of these tasks not only improves the overall performance of the perception system but also enhances the robustness and real-time performance of the system. In this paper, we review the research progress in the field of vision-based multi-task perception for autonomous driving and introduce the methods of traffic object detection, drivable area segmentation, and lane detection in detail. Moreover, we discuss the definition, role, and classification of multi-task learning. In addition, we analyze the design of classical network architectures and loss functions for multi-task perception, introduce commonly used datasets and evaluation metrics, and discuss the current challenges and development prospects of multi-task perception. By analyzing these contents, this paper aims to provide a comprehensive reference framework for researchers in the field of autonomous driving and encourage more research work on multi-task perception for autonomous driving.
Keywords: autonomous driving; deep learning; detection; drivable area segmentation; multi-task learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Research on Road Scene Understanding of Autonomous Vehicles Based on Multi-Task Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;23(13):6238. doi: 10.3390/s23136238. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37448087 Free PMC article.
-
A Multi-Task Road Feature Extraction Network with Grouped Convolution and Attention Mechanisms.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 30;23(19):8182. doi: 10.3390/s23198182. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37837012 Free PMC article.
-
A Multi-Task Network Based on Dual-Neck Structure for Autonomous Driving Perception.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 28;24(5):1547. doi: 10.3390/s24051547. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475082 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey of the Multi-Sensor Fusion Object Detection Task in Autonomous Driving.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 29;25(9):2794. doi: 10.3390/s25092794. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40363232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A survey on 3D object detection in real time for autonomous driving.Front Robot AI. 2024 Mar 6;11:1212070. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1212070. eCollection 2024. Front Robot AI. 2024. PMID: 38510560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liang J., Li Y., Yin G., Xu L., Lu Y., Feng J., Shen T., Cai G. A MAS-Based Hierarchical Architecture for the Cooperation Control of Connected and Automated Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023;72:1559–1573. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3211733. - DOI
-
- Liu H., Yan S., Shen Y., Li C., Zhang Y., Hussain F. Model Predictive Control System Based on Direct Yaw Moment Control for 4WID Self-Steering Agriculture Vehicle. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021;14:175–181. doi: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20211402.5283. - DOI
-
- Kiran B.R., Sobh I., Talpaert V., Mannion P., Sallab A.A.A., Yogamani S., Perez P. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2022;23:4909–4926. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3054625. - DOI
-
- Wang H., Gu J., Wang M. A Review on the Application of Computer Vision and Machine Learning in the Tea Industry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023;7:1172543. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1172543. - DOI
-
- Wei L., Jianping H., Jiaxin L., Rencai Y., Tengfei Z., Mengjiao Y., Jing L. Method for the Navigation Line Recognition of the Ridge without Crops via Machine Vision. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2024;17:230–239. doi: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20241702.7480. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

