Comprehensive circRNA expression profile and hub genes screening during human liver development
- PMID: 40285372
- PMCID: PMC12035923
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2497111
Comprehensive circRNA expression profile and hub genes screening during human liver development
Abstract
Background: Understanding the expression of non-coding RNA in the liver during embryonic development provides important insights into liver diseases. Therefore, we investigated circular RNA (circRNA) roles in human liver development, an unexplored research domain.
Methods: Using high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics, we analysed foetal liver samples across developmental stages (7-20 weeks post-conception). Differentially expressed (DE) genes were identified and subjected to enrichment analysis using Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Disease Ontology (DO). Modular analysis was performed using the Search Tool for Retrieval of Interacting Genes (STRING), followed by construction of a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network using Cytoscape software. The key genes were screened using Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE). The mRNA levels of hub genes were validated using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
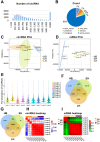
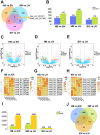
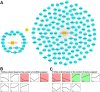
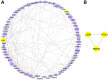
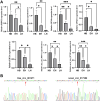
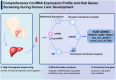
Results: There were 645 DE circRNAs and 5,145 DE mRNAs between human livers at the three growth stages (HB, EH, and LH). It was found that the activity of circRNAs was boosted remarkably in the hepatoblastic stage. Enrichment analysis found they mainly involved in nervous system regulation of liver function, embryonic organ development and digestive system development. In addition, DE circRNAs were primarily involved in the PI3K-AKT, MAPK and calcium pathways, potentially contributing to adult liver diseases. Notably, only hsa_circ_001471 and novel_circ_017382 were simultaneously identified at all stages and were persistently downregulated. A co-expression regulatory network involving these circRNAs was established. Three hub genes (LGR5, FOXL1 and RSPO3) were identified from the PPI network of 167 genes and may play key roles in human liver development. The RT-qPCR validation results were in agreement with the sequencing data.
Conclusions: Our findings provide the first insights into the roles and regulatory networks of circRNAs in human liver development, laying the groundwork for further investigations of molecular and signalling networks.
Keywords: Human liver; circular RNAs; embryonic development; high-throughput RNA sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
