In Vivo Cytosolic Delivery of Biomolecules into Neurons for Super-Resolution Imaging and Genome Modification
- PMID: 40285608
- PMCID: PMC12224921
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202501033
In Vivo Cytosolic Delivery of Biomolecules into Neurons for Super-Resolution Imaging and Genome Modification
Abstract
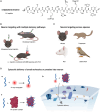
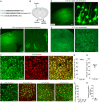
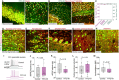
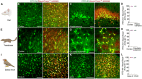
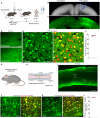
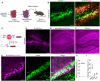
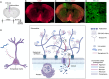
Efficient delivery of biomolecules into neurons has significant impacts on therapeutic applications in the central nervous system (CNS) and fundamental neuroscience research. Existing viral and non-viral delivery methods often suffer from inefficient intracellular access due to the endocytic pathway. Here, a neuron-targeting and direct cytosolic delivery platform is discovered by using a 15-amino-acid peptide, termed the N1 peptide, which enables neuron-specific targeting and cytosolic delivery of functional biomolecules. The N1 peptide initially binds hyaluronan in the extracellular matrix and subsequently passes the membrane of neurons without being trapped into endosome. This mechanism facilitates the efficient delivery of cell-impermeable and photo-stable fluorescent dye for super-resolution imaging of dendritic spines, and functional proteins, such as Cre recombinase, for site-specific genome modification. Importantly, the N1 peptide exhibits robust neuronal specificity across diverse species, including mice, rats, tree shrews, and zebra finches. Its targeting capability is further demonstrated through various administration routes, including intraparenchymal, intrathecal, and intravenous (i.v.) injections after blood-brain barrier (BBB) opening with focused ultrasound (FUS). These findings establish the N1 peptide as a versatile and functional platform with significant potential for bioimaging and advanced therapeutic applications.
Keywords: across species; genome modification; neuron specific targeting; peptides; super‐resolution imaging.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nucleic Acid Nanocapsules as a New Platform to Deliver Therapeutic Nucleic Acids for Gene Regulation.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jul 1;58(13):1951-1962. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5c00126. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 40491030
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Intranasal delivery of temozolomide and desloratadine for brain tumour therapy: A cellular study on nasal epithelial toxicity, transport, and permeability.J Pharm Sci. 2025 Jul;114(7):103795. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2025.103795. Epub 2025 Apr 14. J Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40239838
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malezieux M., Klein A. S., Gogolla N., Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 46, 211. - PubMed
-
- Wang B., Torok Z., Duffy A., Bell D. G., Wongso S., Velho T. A. F., Fairhall A. L., Lois C., Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 1176. - PubMed
-
- Garcia‐Chica J., DParaiso W. K., Tanabe S., Serra D., Herrero L., Casals N., Garcia J., Ariza X., Quader S., Rodriguez‐Rodriguez R., Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1617. - PubMed
-
- Dejanovic B., Sheng M., Hanson J. E., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2024, 23, 23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
