PANoptosis: a potential target of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 40285923
- PMCID: PMC12167338
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-025-02089-x
PANoptosis: a potential target of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Abstract
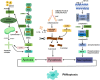
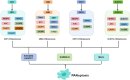
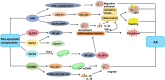
PANoptosis is a newly discovered cell death pathway triggered by the innate immunizer, which in turn promotes the assembly of the PANoptosome and activates downstream effectors. As a special cell death mode, it is characterized by apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis at the same time; therefore, it is not feasible to inhibit PANoptosis by suppressing a single cell death pathway. However, active ingredients targeting the PANoptosome can effectively inhibit PANoptosis.Given the importance of cell death in disease, targeting PANoptosis would be an important therapeutic tool. Previous studies have focused more on infectious diseases and cancer, and the role of PANoptosis in the cardiovascular field has not been comprehensively addressed. While ASCVD is the number one killer of cardiovascular diseases, it is important to explore new targets to determine future research directions. Therefore, this review focuses on the assembly of PANoptosome, the molecular mechanism of PANoptosis, and the related mechanisms of PANoptosis leading to ASCVD such as myocardial infarction, ischemic cardiomyopathy and ischemic stroke, in order to provide a new perspective for the prevention and treatment of ASCVD.
Keywords: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; Inflammation; PANoptosis; PANoptosome; PCD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PANoptosis: a potential new target for programmed cell death in breast cancer treatment and prognosis.Apoptosis. 2024 Apr;29(3-4):277-288. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01904-7. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38001342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PANoptosis: a novel target for cardiovascular diseases.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2024 Aug;45(8):739-756. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2024.06.002. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39003157 Review.
-
Global trends in PANoptosis research: bibliometrics and knowledge graph analysis.Apoptosis. 2024 Feb;29(1-2):229-242. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01889-3. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 37751105
-
PANoptosis: Cross-Talk Among Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis in Neurological Disorders.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jun 19;18:8131-8140. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S526158. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40551989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining PANoptosis: Biochemical and Mechanistic Evaluation of Innate Immune Cell Death Activation.Curr Protoc. 2024 Jul;4(7):e1112. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.1112. Curr Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39073015 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials