Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel Hydrazide and Hydrazone Derivatives: Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Potential in Preclinical Models
- PMID: 40286066
- PMCID: PMC11990862
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30071472
Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel Hydrazide and Hydrazone Derivatives: Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Potential in Preclinical Models
Abstract
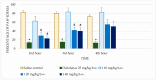
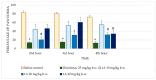
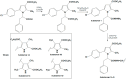
Hydrazones, characterized by their C=N-NH functional group, are promising candidates in medicinal chemistry due to their ability to interact with biological targets. This study evaluated the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of N-pyrrolylcarbohydrazide (1) and four pyrrole hydrazone derivatives (1A-D) in male Wistar rats (6 weeks old). Anti-inflammatory activity was assessed using a carrageenan-induced paw edema model, while formalin, tail flick, and paw withdrawal tests evaluated analgesia. Compound 1 exhibited dose-dependent anti-inflammatory activity. At 20 mg/kg, significant edema reductions were observed at the 2nd (p = 0.035) and 3rd hours (p = 0.022), while at 40 mg/kg, reductions remained significant at the 2nd (p = 0.008) and 3rd hours (p = 0.046). Compound 1A showed pronounced effects at 20 mg/kg at the 2nd (p = 0.005), 3rd (p < 0.001), and 4th hours (p = 0.004). Other compounds demonstrated minimal or no activity. Analgesic evaluation revealed that at 40 mg/kg, compound 1 significantly reduced paw-licking time in the second phase (p = 0.038). Compounds 1B, 1C, and 1D exhibited transient effects in the first phase only (p < 0.05). Compound 1A lacked significant analgesic activity. The findings suggest that structural modifications may enhance efficacy for broader therapeutic applications.
Keywords: formalin model; hydrazones; paw edema; paw withdrawal; tail-flick.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biological Screening of Novel Structural Analog of Celecoxib as Potential Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Agent.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Apr 5;55(4):93. doi: 10.3390/medicina55040093. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 30959829 Free PMC article.
-
The analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of WIN-34B, a new herbal formula for osteoarthritis composed of Lonicera japonica Thunb and Anemarrhena asphodeloides BUNGE in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Sep 15;131(2):485-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.07.025. Epub 2010 Jul 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20643199
-
In-silico based Designing of benzo[d]thiazol-2-amine Derivatives as Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Agents.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2024;23(4):230-260. doi: 10.2174/0118715230296273240725065839. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39162282
-
Design and synthesis of novel dithiazole carboxylic acid Derivatives: In vivo and in silico investigation of their Anti-Inflammatory and analgesic effects.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Mar;144:107120. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107120. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38219479
-
Thiazolidin-4-one and hydrazone derivatives of capric acid as possible anti-inflammatory, analgesic and hydrogen peroxide-scavenging agents.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2011 Aug;26(4):546-52. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2010.535796. Epub 2010 Dec 20. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21171895
References
-
- Ali A., Khalid M., Abid S., Iqbal J., Tahir M.N., Rauf Raza A., Zukerman-Schpector J., Paixao M.W. Facile synthesis, crystal growth, characterization and computational study of new pyridine-based halogenated hydrazones: Unveiling the stabilization behavior in terms of noncovalent interactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020;34:e5399. doi: 10.1002/aoc.5399. - DOI
-
- Ribeiro N., Correia I. A review of hydrazide-hydrazone metal complexes’ anti-tumor potential. Front. Chem. Biol. 2024;3:1398873. doi: 10.3389/fchbi.2024.1398873. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

