Influence of Copigmentation and Encapsulation on Stability and Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanins from Blue and Pink Cornflower (Centaurea cyanus L.) Flowers
- PMID: 40286073
- PMCID: PMC11990276
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30071467
Influence of Copigmentation and Encapsulation on Stability and Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanins from Blue and Pink Cornflower (Centaurea cyanus L.) Flowers
Abstract
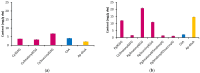
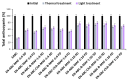
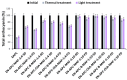
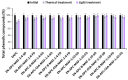
The aim of this study was to determine the optimal conditions for copigmentation and encapsulation of anthocyanins extracted from blue and pink cornflower (Centaurea cyanus L.) flowers and to produce encapsulates resistant to environmental factors. Extracts rich in anthocyanins were encapsulated using spray-drying and sublimation techniques. Baicalin and chlorogenic acid were successfully used as copigmentation agents for blue and pink cornflower anthocyanins. The extracts and encapsulates obtained were subjected to stability tests to assess the stability of color and changes in total anthocyanins content, total phenolic compounds content, and antioxidant activity under exposure to high temperature and UV radiation. The developed encapsulation method effectively protects anthocyanins from adverse environmental conditions. The obtained preparations were characterized by a high content of anthocyanins and phenolic compounds as well as a strong antioxidant potential. The highest stability was demonstrated by anthocyanin encapsulates isolated from the pink flowers of the cornflower, obtained by spray-drying with the addition of a copigment (chlorogenic acid or baicalin) and with a weight ratio of anthocyanin extract to carrier of 1:10. The results of this study suggest that anthocyanin preparations from cornflower, after encapsulation and copigmentation with baicalin or chlorogenic acid, can be used as stable colorants in the food industry as well as functional ingredients providing high levels of antioxidant activity.
Keywords: anthocyanins; copigmentation; cornflower; encapsulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemical study, antioxidant, anti-hypertensive, and cytotoxic/cytoprotective activities of Centaurea cyanus L. petals aqueous extract.Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Aug;118:439-453. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.05.046. Epub 2018 May 19. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29787846
-
Stabilization of Black Rice (Oryza Sativa, L. Indica) Anthocyanins Using Plant Extracts for Copigmentation and Maltodextrin for Encapsulation.J Food Sci. 2019 Jul;84(7):1712-1720. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14688. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Food Sci. 2019. PMID: 31242535
-
Components of protocyanin, a blue pigment from the blue flowers of Centaurea cyanus.Phytochemistry. 2005 Jul;66(13):1607-13. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.04.002. Phytochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16005311
-
Combination of copigmentation and encapsulation strategies for the synergistic stabilization of anthocyanins.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021 Jul;20(4):3164-3191. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12772. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021. PMID: 34118125 Review.
-
Stabilizing and Modulating Color by Copigmentation: Insights from Theory and Experiment.Chem Rev. 2016 May 11;116(9):4937-82. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00507. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 26959943 Review.
Cited by
-
Intelligent pH-responsive films based on natural blueberry anthocyanins: A non-destructive monitoring system for the freshness of aquatic products with prospective smartphone compatibility.Food Chem X. 2025 May 26;28:102587. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102587. eCollection 2025 May. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40511338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grajeda-Iglesias C., Figueroa-Espinoza M., Barouh N., Barea B., Fernandes A., de Freitas V., Salas E. Isolation and characterization of anthocyanins from Hibiscus sabdariffa flowers. J. Nat. Prod. 2016;79:1709–1718. - PubMed
-
- Kanha N., Regenstein J.M., Surawang S., Pitchakarn P., Laokuldilok T. Properties and kinetics of the in vitro release of anthocyanin-rich microcapsules produced through spray and freeze-drying complex coacervated double emulsions. Food Chem. 2021;15:340. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

