Neuropilin Antagonists (NRPas) Block the Phosphorylation of the Cancer Therapeutic Key Factor p38α Kinase Triggering Cell Death
- PMID: 40286084
- PMCID: PMC11990468
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30071494
Neuropilin Antagonists (NRPas) Block the Phosphorylation of the Cancer Therapeutic Key Factor p38α Kinase Triggering Cell Death
Abstract
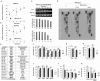
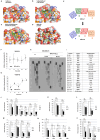
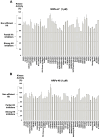
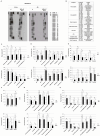
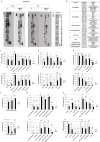
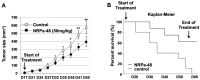
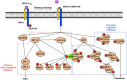
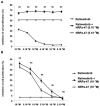
Neuropilin-1 is henceforth a relevant target in cancer treatment; however, its way of action remains partly elusive, and the development of small inhibitory molecules is therefore required for its study. Here, we report that two small-sized neuropilin antagonists (NRPa-47 and NRPa-48), VEGF-A165/NRP-1 binding inhibitors, are able to decrease VEGF-Rs phosphorylation and to modulate their downstream cascades in the triple-negative breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231). Nevertheless, NRPas exert a divergent pathway regulation of MAPK phosphorylation, such as JNK-1/-2/-3, ERK-1/-2, and p38β/γ/δ-kinases, as well as their respective downstream targets. However, NRPa-47 and NRPa-48 apply a common down-regulation of the p38α-kinase phosphorylation and their downstream targets, emphasising its central regulating role. More importantly, none of the 40 selected kinases, including SAPK2a/p38α, are affected in vitro by NRPas, strengthening their specificity. Taken together, NRPas induced cell death by the down-modulation of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins, cell death receptors and adaptors, heat shock proteins (HSP-27/-60/-70), cell cycle proteins (p21, p27, phospho-RAD17), and transcription factors (p53, HIF-1α). In conclusion, we showed for the first time how NRPas may alter tumour cell signalling and contribute to the down-modulation of the cancer therapeutic key factor p38α-kinase phosphorylation. Thus, the efficient association of NRPas and p38α-kinase inhibitor strengthened this hypothesis.
Keywords: VEGF; breast cancer; neuropilin antagonists; neuropilin-1; p38α kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Nicolas Lopez and Yves Lepelletier were employed by the company W-MedPhys. All the authors have read the manuscript, concur with its content, and state that its content has not been submitted elsewhere. The authors declare no competing financial interests and no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

