Goutweed (Aegopodium podagraria L.)-An Edible Weed with Health-Promoting Properties
- PMID: 40286209
- PMCID: PMC11990176
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30071603
Goutweed (Aegopodium podagraria L.)-An Edible Weed with Health-Promoting Properties
Abstract
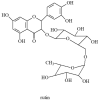
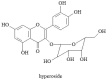
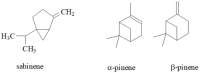
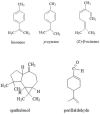
Goutweed (Aegopodium podagraria L.) is a species of medicinal perennial in the celery family (Apiaceae), also considered an edible plant with medicinal effects and high nutritional value. In traditional folk medicine, it was known as a remedy for gout (arthritis) and also used to relieve rheumatism or sciatica. The botanical characteristics, occurrence, nutritional composition, and traditional and present-day applications of this plant are discussed. Furthermore, the important specific plant metabolites including organic acids and their derivatives, flavonoids, coumarins, polyacetylenes and terpene components of essential oil are presented and their biological activity is described. The valuable medicinal properties of Aegopodium podagria L. include anti-inflammatory, antirheumatic, antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, diuretic, sedative and protective effects on the kidneys and liver. The aim of this paper was to describe, on the basis of the available literature, the chemical composition, bioactivity and health-promoting properties of this wild edible plant. The information obtained is described and summarized in tables.
Keywords: Aegopodium podagraria L.; bioactivity; biologically active compounds; goutweed; ground elder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Kyrbassova E.A., Baitasheva G.U., Danilov M.P., Dyuskaliyeva G.U., Abdrasulova Z., Adenova B.E., Saparov A. Anatomical-Morphological and Phytochemical Study of Medicinal Plant Aegopodium podagraria L. Growing in Kazakhstan. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2018;10:689–697.
-
- Valyova M., Tashev A., Stoyanov S., Yordanova S., Ganeva Y. In Vitro Free-Radical Scavenging Activity of Aegopodium podagraria L. and Orlaya grandiflora (L.) Hoffm. (Apiaceae) J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2016;51:271–274.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

