Roles of chromosomal and gonadal sex in the fetal and placental responses to maternal food restriction in mice
- PMID: 40286295
- PMCID: PMC12085225
- DOI: 10.1093/molehr/gaaf015
Roles of chromosomal and gonadal sex in the fetal and placental responses to maternal food restriction in mice
Abstract
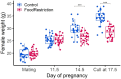
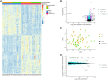
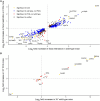
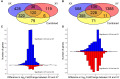
It is hypothesized that male fetuses are more vulnerable to in utero insults than females due to different growth strategies, and that the placenta contributes to these sex differences. We examined sex differences in the fetal and placental responses to maternal food restriction (∼60% of ad libitum) beginning mid-gestation (Day 11.5). To dissect the roles of chromosomal and gonadal sex, we used the Four Core Genotypes mouse model, which combines deletion of the testis-determining Sry gene from the Y chromosome and autosomal insertion of the Sry gene, such that XX gonadal males and XY gonadal females are produced in addition to XX females and XY males. Food restriction reduced fetal and placental weights but had no effect on the number of viable conceptuses. However, this effect did not differ between gonadal male and female, or between XX and XY, conceptuses. Sex differences in gene expression in both the labyrinth and the combined junctional zone/decidua, as assessed by RNA sequencing, were due entirely to chromosomal sex and not gonadal sex. Food restriction affected the expression of 525 and 665 genes in the labyrinth and the junctional zone/decidua, respectively. However, these effects of food restriction did not differ by gonadal or chromosomal sex when assessed for statistical interactions. In contrast, when analyzing XX and XY placentas separately, hundreds of genes were affected by food restriction in one sex but not in the other, including hundreds of genes not found to be significant in the combined analyses. However, estimated effect sizes were generally similar for XX and XY placentas, suggesting that these sex-stratified analyses greatly exaggerated the extent of sex-dependent responses. Overall, we did not find evidence of the hypothesized sex differences in fetal growth strategy and found that sex differences in placental gene expression were largely due to chromosomal sex.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; decidua; junctional zone; labyrinth; malnutrition; placenta; sex differences; transcriptomics.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures






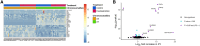
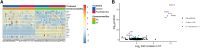


Comment in
-
Permutation tests to assess sex differences in omics data.Mol Hum Reprod. 2025 Jul 3;31(3):gaaf047. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaaf047. Mol Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40973219
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

