Long-term efficacy and safety of different biologics in treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A network meta-analysis
- PMID: 40286594
- PMCID: PMC12056389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2025.101633
Long-term efficacy and safety of different biologics in treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Direct comparison of the long-term effectiveness and safety of biologics for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (CRSwNP) is lacking. The study aimed to compare the long-term efficacy and safety of various biologics in the management of CRSwNP.
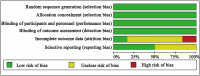
Methods: The PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched from database inception to March 2024, to identify all relevant literature on the use of biologics for CRSwNP. The research protocol was registered on PROSPERO.Two independent reviewers screened the studies, extracted the data, and performed a quality assessment using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. Network meta-analysis was conducted using STATA 17.0 and Review Manager (Version 5.3).
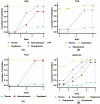
Results: Six studies with a minimum follow-up period of 52-weeks were analyzed, demonstrating the superior long-term efficacy of dupilumab compared to the other three biologics. The surface under the cumulative ranking curve were 100% for Nasal Polyp Score (NPS), 72.7% for Sino-Nasal Outcome Test-22 (SNOT-22), 94.6% for Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), and 100% for Nasal Congestion Score (NCS). In the comparison of NPS, dupilumab showed improvements of 1.84 (95% Confidence Interval [95% CI 0.78, 2.91]) over mepolizumab and 2.31 (95% CI 0.99, 3.63) over benralizumab. Among the symptom scores evaluated, only dupilumab achieved a significant improvement in NCS compared to benralizumab, with an improvement of 0.74 (95% CI 0.86, 1.19). No significant differences in adverse events was observed between biologics treatment or versus placebo.
Conclusion: Treatment with dupilumab in patients with CRSwNP has shown superior long-term efficacy in reducing NPS and various symptom scores compared to other biologics. However, the results should be interpreted with caution due to the heterogeneity of patient characteristics across the included studies (e.g., disease severity, history of surgery, use of oral corticosteroids).
Keywords: Biologics; Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; Long-term efficacy; Network meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier España S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chen S., Zhou A., Emmanuel B., Thomas K., Guiang H. Systematic literature review of the epidemiology and clinical burden of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020;36:1897–1911. - PubMed
-
- Amedee R.G. Prevalence of polyp recurrence after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2017;31:278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

