MMP1-induced NF-κB activation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and sacituzumab govitecan resistance in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer
- PMID: 40287412
- PMCID: PMC12033297
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07615-y
MMP1-induced NF-κB activation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and sacituzumab govitecan resistance in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer
Abstract
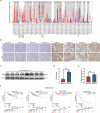
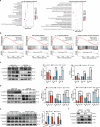
Sacituzumab govitecan (SG), a novel antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), shows promise in the treatment of breast cancer (BC); however, drug resistance limits its clinical application. Matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1), which is overexpressed in many tumor types, plays a key role in tumor metastasis and drug resistance. The involvement of MMP1 in SG resistance in metastatic hormone receptor-positive (HR + ) BC has not been previously reported. In this study, we employed various in vitro and in vivo approaches to investigate the role of MMP1 in SG resistance in BC. MMP1 expression was manipulated in different BC cell lines through lentiviral transfection and small interfering RNA techniques. Key methodologies included Western blot, quantitative reverse transcription PCR, and RNA sequencing to assess marker expression and identify differentially expressed genes. Functional assays were conducted to evaluate cell viability, proliferation, invasion, and migration. In vivo, a cell-derived xenograft model in nude mice was utilized to assess tumor growth and drug response. Bioinformatics analyses further explored MMP1 expression and its clinical relevance across different cancer types. Our findings indicate that MMP1 is overexpressed by approximately 30-fold in HR + BC tissues and is associated with poorer prognosis among HR + BC patients. Furthermore, our analysis reveals that HR + BC with high MMP1 expression displays resistance to SG, supporting the hypothesis that MMP1 plays a key role in regulating ADC resistance. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that MMP1 can activate the NF-κB pathway, which subsequently influences the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, thereby contributing to SG resistance. Ultimately, our research underscores the potential of MMP1 as a therapeutic target and biomarker, facilitating personalized treatment strategies that could enhance patient outcomes in BC therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Ethical approval: This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants or their legal guardians prior to sample collection and data acquisition. The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-sen University.
Figures






Similar articles
-
RelB sustains endocrine resistant malignancy: an insight of noncanonical NF-κB pathway into breast Cancer progression.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Aug 17;18(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00613-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32807176 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in paclitaxel-resistant breast cancer cells via regulating nuclear factor kappa B and F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 11.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):11506-11519. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2009963. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34905470 Free PMC article.
-
Sacituzumab govitecan, an antibody-drug conjugate targeting trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2, shows cytotoxic activity against poorly differentiated endometrial adenocarcinomas in vitro and in vivo.Mol Oncol. 2020 Mar;14(3):645-656. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12627. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31891442 Free PMC article.
-
Sacituzumab govitecan: past, present and future of a new antibody-drug conjugate and future horizon.Future Oncol. 2022 Sep;18(28):3199-3215. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0407. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Future Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36069628 Review.
-
Sacituzumab Govitecan-hziy in Breast Cancer.Am J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jul 1;45(7):279-285. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000919. Epub 2022 May 12. Am J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35728046 Review.
References
-
- Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Miller KD, Kramer JL, Newman LA, Minihan A, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:524–41. - PubMed
-
- Gennari A, Andre F, Barrios CH, Cortes J, de Azambuja E, DeMichele A, et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:1475–95. - PubMed
-
- Yuan P, Hu X, Sun T, Li W, Zhang Q, Cui S, et al. Eribulin mesilate versus vinorelbine in women with locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: a randomised clinical trial. Eur J Cancer. 2019;112:57–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

