Investigation of cadmium removal using tin oxide nanoflowers through process optimization, isotherms and kinetics
- PMID: 40287588
- PMCID: PMC12033334
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-99636-y
Investigation of cadmium removal using tin oxide nanoflowers through process optimization, isotherms and kinetics
Abstract
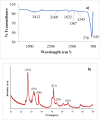
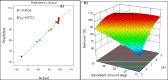
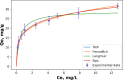
The present study demonstrates a treatment approach that utilizes flower-shaped tin oxide nanoparticles for the removal of cadmium from synthetic wastewater by adsorption. Tin oxide nanoparticles were synthesized using a simple and eco-friendly method and employed for the removal of cadmium ions from wastewater. The nanoflowers were successfully characterized using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, X-Ray Diffraction Analysis, Scanning Electron Microscope and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area analysis. The batch adsorption process was optimized by response surface methods to investigate the influential parameters of the adsorption process. Optimal removal efficacy was achieved at a pH value of 9.0, a mixing time of 20 min, and an adsorbent amount of 15 mg. The results indicated that the adsorbent achieved a maximum removal efficiency of 99.14 ± 0.10% for Cd(II)ions in domestic wastewater. The adsorption equilibrium process was elucidated by Langmuir, Freundlich, Sips and Toth isotherm models using nonlinear regression. In addition, error functions such as Chi-square (X2, Average Relative Error (ARE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) and HYBRID were used to test the validity of the nonlinear models. The results indicated that the Sips model, with an R2 value of 0.9894, accurately matched the experimental data and adsorption capacity of 57.12 mg g- 1 for Cd(II) was calculated respectively. The sorption kinetics were well characterized by a pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The results demonstrated that adsorption of cadmium onto the surface of SnO2 nanoparticles is influenced by both monolayer adsorption and multi-site interactions. These findings indicate that SnO2 nanoparticles are suitable for removing cadmium from aqueous solutions in batch processes.
Keywords: Adsorption isotherms; Experimental design; Heavy metal removal, domestic wastewater, nanoflowers.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microwave-assisted synthesis of γ-alooh nanoflowers as an adsorbent for cadmium removal from domestic wastewater.Environ Monit Assess. 2024 Oct 1;196(10):996. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13175-z. Environ Monit Assess. 2024. PMID: 39352559
-
Statistical analyses on effective removal of cadmium and hexavalent chromium ions by multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs).Heliyon. 2020 Jun 8;6(6):e04174. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04174. eCollection 2020 Jun. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32551395 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium and copper heavy metal treatment from water resources by high-performance folic acid-graphene oxide nanocomposite adsorbent and evaluation of adsorptive mechanism using computational intelligence, isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic analyses.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Dec;27(35):43999-44021. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10175-7. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32748352
-
The application of Rumex Abysinicus derived activated carbon/bentonite clay/graphene oxide/iron oxide nanocomposite for removal of chromium from aqueous solution.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):19280. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70238-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39164377 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles impregnated on apple pomace to enhanced adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Jul;22(14):10919-29. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4276-2. Epub 2015 Mar 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25772868
References
-
- Kavisri, M. et al. Adsorption isotherm, kinetics and response surface methodology optimization of cadmium (Cd) removal from aqueous solution by Chitosan biopolymers from cephalopod waste. J. Environ. Manage.335, 117484 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Fanfani, A. et al. Cadmium in biological samples and site-specific cancer risk and mortality: A systematic review of original articles and meta-analyses. Cancer Epidemiol.10255010.1016/J.CANEP.2024.102550 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Bracher, C. et al. Tracing the fate of phosphorus fertilizer derived cadmium in soil-fertilizer-wheat systems using enriched stable isotope labeling. Environ. Pollut.287, 117314 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Arabkhani, P. & Asfaram, A. A novel biowaste-derived magnetic adsorbent for efficient removal of cadmium, Cobalt and strontium ions from industrial wastewater. Inorg. Chem. Commun.174, 113956 (2025).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

