Global, regional, and national burden of disease analysis on paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction in adults aged 65 and over from 1990 to 2021, with projections for 2030: a Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 analysis
- PMID: 40287622
- PMCID: PMC12032820
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-025-03904-0
Global, regional, and national burden of disease analysis on paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction in adults aged 65 and over from 1990 to 2021, with projections for 2030: a Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the burden and trends of paralytic ileus and bowel obstruction in individuals aged ≥ 65 years, offering insights into prevention, treatment, and healthcare policy.
Methods: Data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 were used to analyze paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction by demographics, year, country/region, and Socio-Demographic Index (SDI). The statistical methods included Joinpoint regression, decomposition analysis, and Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort modeling.
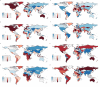
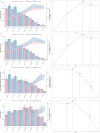
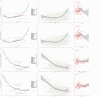
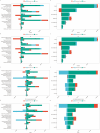
Results: In 2021, the global age-standardized incidence of paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction among the elderly was 643.45 cases per 100,000 individuals. The corresponding prevalence was 24.05 per 100,000 individuals, with disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of 294.01 per 100,000 person-years and a mortality rate of 20.55 per 100,000 individuals. Between 1990 and 2021, the age-standardized incidence and prevalence of paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction in the elderly gradually increased, while age-standardized DALYs and mortality consistently declined. Despite similar trends observed across both genders, the disease burden increased with age and was more pronounced in males than in females. Furthermore, the age-standardized incidence and prevalence of these conditions increased with SDI, whereas mortality and DALYs decreased. By 2030, the incidence and prevalence are expected to continue increasing, whereas mortality and DALYs are expected to decrease.
Conclusions: Despite the consistent decrease in mortality and DALYs associated with paralytic ileus and bowel obstruction in the elderly population aged ≥ 65 years, their incidence and prevalence continue to increase annually. This underscores the importance of improving preventive measures, early screening, and treatment efforts to address this pressing public health challenge.
Keywords: Disease burden; Older adults; Paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction; Projections; Trend analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The global, regional, and national burden of paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction, 1990 to 2021: a cross-sectional analysis from the 2021 global burden of disease study.Int J Surg. 2025 Feb 1;111(2):1773-1787. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002189. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39784557
-
The global burden of vascular intestinal diseases: results from the 2021 Global Burden of Disease Study and projections using Bayesian age-period-cohort analysis.Environ Health Prev Med. 2024;29:71. doi: 10.1265/ehpm.24-00206. Environ Health Prev Med. 2024. PMID: 39662956 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal trends in hernia disease burden and health workforce correlations in aging populations: a global analysis with projections to 2050.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 25;25(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03916-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40281398 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of elderly myocarditis (1992-2021) and projections of future disease burden trends.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025 Mar 24;37(1):102. doi: 10.1007/s40520-025-02979-9. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025. PMID: 40128382 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burdens of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia in the elderly population from 1999 to 2019: A trend analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Ibrain. 2024 Sep 22;10(4):488-499. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12181. eCollection 2024 Winter. Ibrain. 2024. PMID: 39691425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global burden of paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction, 1990-2021: a GBD 2021 analysis.J Health Popul Nutr. 2025 Aug 18;44(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-01045-4. J Health Popul Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40826126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liang Q, Wang JW, Bai YR, et al. Targeting TRPV1 and TRPA1: a feasible strategy for natural herbal medicines to combat postoperative ileus. Pharmacol Res. 2023;196:106923. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths S, Glancy DG. Intestinal obstruction(J). Surg (Oxford). 2023;41(1):47–54.
-
- Wang Y, Huang Y, Chase RC, et al. Global burden of digestive diseases: a systematic analysis of the global burden of diseases study, 1990 to 2019(J). Gastroenterology. 2023;165(3):773–83. e15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

