Integrating team-based and peer-teaching strategies for standardized dental residency: a path to active learning and professional growth
- PMID: 40287670
- PMCID: PMC12032740
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-025-07023-y
Integrating team-based and peer-teaching strategies for standardized dental residency: a path to active learning and professional growth
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of an integrated Team-Based Learning (TBL) and Peer Teaching (PT) model in enhancing theoretical knowledge, clinical competencies, and engagement among dental residents, offering insights for improving stomatology education.
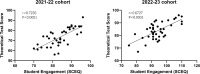
Methods: This study was conducted at the affiliated stomatology hospital of Guangzhou medical university between 2021 and 2023. The 2021-22 cohort (n = 39) students received a traditional teacher-centered approach, whereas the 2022-23 cohort (n = 43) underwent a combined TBL and PT approach. Following a three-month training period, theoretical exams and OSCE were administered. Student engagement was evaluated using the SCEQ, and satisfaction was assessed through SSS. Data were analyzed using independent t-tests, Mann-Whitney U tests, and χ² tests, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05.
Results: No significant baseline differences were observed in demographics. TBL + PT cohort demonstrated significantly higher theoretical test scores and OSCE performance in most assessed skills, including pulpotomy, tooth preparation, incision and suturing, and patient intake. Engagement scores were also significantly higher in the domains of emotional engagement and participation/interaction, and overall student satisfaction improved, particularly regarding teaching quality and student-centric learning methods. Word cloud analyses of student feedback revealed a stronger emphasis on collaboration, participation, and innovation in the TBL + PT cohort compared to the traditional group.
Conclusions: Incorporating Team-Based Learning and Peer Teaching into standardized dental residency training markedly enhanced theoretical knowledge, clinical proficiencies, and learner engagement. This instructional strategy improved residents' technical competencies and cultivated stronger team collaboration, communication, and higher satisfaction levels, offering a promising alternative to traditional teaching for residency training in oral medicine.
Keywords: Oral medicine; Peer teaching; Standardized residency training; Student engagement; Team-based learning.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Study compliant/adhered to Helsinki Declaration. Study received ethical approval by the ethics committee of the affiliated stomatological hospital of Guangzhou medical university (Approval Number: JXYJ20250303001). Informed oral consent to participate was obtained from all participants prior to their enrollment in the study. The ethics committee approved the use of oral consent as sufficient for this study due to it primarily involved routine educational activities and surveys without any invasive procedures or interventions. Consent for publication: Not applicable. There are no details on individuals reported within the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of scaffolded case-based learning in anesthesiology residency training: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Med Educ. 2025 May 8;25(1):672. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07236-1. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40340724 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Team-based learning for psychiatry residents: a mixed methods study.BMC Med Educ. 2013 Sep 11;13:124. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-13-124. BMC Med Educ. 2013. PMID: 24025540 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Team-Based Learning Pedagogy for Internal Medicine Ambulatory Resident Teaching.J Grad Med Educ. 2015 Dec;7(4):643-8. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-14-00790.1. J Grad Med Educ. 2015. PMID: 26692979 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of TBL teaching on nursing students' knowledge, practical skills and core ability: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nurse Educ Pract. 2024 Oct;80:104125. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2024.104125. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Nurse Educ Pract. 2024. PMID: 39317089
-
Comparing the effects of team-based and problem-based learning strategies in medical education: a systematic review.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Feb 22;24(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05107-9. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38388937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu ZY, et al. Comparison of dental education and professional development between Mainland China and North America. Eur J Dent Educ. 2010;14(2):106–12. - PubMed
-
- Komabayashi T, et al. Education of dentists in China. Int Dent J. 2006;56(5):272–6. - PubMed
-
- Roudnitsky E, et al. Influence of residency training program on pursuit of academic career and academic productivity among oral and maxillofacial surgeons. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;80(2):380–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

