GRB2 promotes brain metastasis in HER2-positive breast cancer by regulating the Ras/MAPK pathway
- PMID: 40289214
- PMCID: PMC12034778
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-99685-3
GRB2 promotes brain metastasis in HER2-positive breast cancer by regulating the Ras/MAPK pathway
Abstract
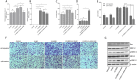
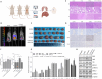
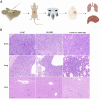
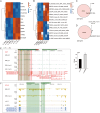
Brain metastasis is emerging as the most serious concern for breast cancer patients. HER2-positive breast cancer is more prone to undergo brain metastasis than other subtypes; notably, there has been little improvement in the treatment of brain metastasis .Our study confirmed the relevance of HER2 status to brain metastasis risk via clinical data analysis and revealed that exerts GRB2 tumorigenic effects by regulating the Ras/MAPK pathway in vivo and in vitro. Both an in situ injection model and a direct cerebral injection model were used to explore the ability of GRB2 to promote the brain metastasis. Results indicated that HER2- positive is a risk factor for brain metastasis according to clinical data. GRB2 enhances proliferation, migration, and invasion while suppressing apoptosis in HER2-positive breast cancer cells in vitro, primarily by regulating phosphorylation and alternative splicing of key proteins within the Ras/MAPK pathway. Notably, tumor cells were able to cross the blood‒brain barrier in both models assessed in this study. Thus, GRB2 is an oncogenic factor that contributes to the malignancy of HER2-positive breast cancer, GRB2 and HER2 can synergistically promote tumor cell penetration of the blood‒brain barrier and induce metastasis.
Keywords: Brain metastasis; GRB2; HER2-positive breast cancer; Ras/MAPK pathway.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics declarations: All experiments involving human participants and/or human tissue samples were conducted in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations, including the Declaration of Helsinki. All experimental protocols were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Approval ID: K-2024018).Informed consent was obtained from all participants and/or their legal guardian(s) prior to their inclusion in the study.All experiments involving live vertebrates were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Newlong Youshu Technology (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd (Approval ID: YS-m202501001). All procedures were performed in accordance with the Chinese Guidelines for Ethical Review of Laboratory Animal Welfare (GB/T 35892 − 2018) and international ethical guidelines for animal research. This study adheres to the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0 ( https://arriveguidelines.org ) to ensure comprehensive reporting of experimental methodology. Efforts were made to minimize animal suffering and reduce the number of animals used, following the principles of Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement (3Rs).
Figures

References
-
- Kingwell, K. Metabolic target for brain metastasis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20 (6), 426 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Corti, C. et al. Targeting brain metastases in breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev.103, 102324 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Faure, C. et al. Allosteric Inhibition of HER2 by Moesin-Mimicking compounds targets HER2-Positive cancers and brain metastases. Cancer Res.81 (21), 5464–5476 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022TCYCLHY/The Tianchi Talents-Young Doctor Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region
- 2021D01C41 1/Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang
- ZYYD2022/The Guiding Funds of Central Government for Supporting the Development of the Local Science and Technology
- 2023 TSLJ 0038/Tianshan Talents-Leading Talents in Science and Technology Innovation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

