Mechanistic insights into proteasome inhibitor MG132 induced apoptosis in melanoma A375 cells
- PMID: 40289224
- PMCID: PMC12034790
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-99151-0
Mechanistic insights into proteasome inhibitor MG132 induced apoptosis in melanoma A375 cells
Abstract
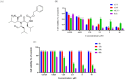
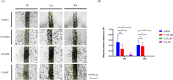
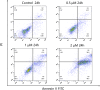
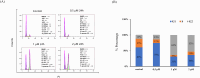
Despite advancements in melanoma therapy, the prognosis remains unfavorable for many patients. The proteasome inhibitor MG132 has shown therapeutic potential through pathway regulation, yet its precise mechanisms in melanoma require systematic elucidation. Using A375 melanoma cells, we conducted multi-modal investigations combining cytotoxicity assessment (CCK8), migration analysis (wound healing), apoptosis quantification (flow cytometry), and proteomic profiling (western blot) to dissect MG132's molecular mechanisms. Our findings revealed MG132's potent anti-tumor activity with an IC50 of 1.258 ± 0.06 µM, significantly suppressing cellular migration at therapeutic concentrations. Apoptosis assays demonstrated concentration-dependent effects, with 2 µM treatment inducing early apoptosis in 46.5% and total apoptotic response in 85.5% of cells within 24 h. Mechanistic studies uncovered MG132's dual regulatory capacity: (1) Through MDM2 inhibition, it activated p53/p21/caspase-3 axis while suppressing CDK2/Bcl2, triggering cell cycle arrest and DNA damage cascades; (2) MAPK pathway activation emerged as a critical apoptosis driver. Notably, western blot analysis established dose-responsive modulation of these molecular targets, confirming pathway specificity. Our results position MG132 as a multi-target agent capable of simultaneously disrupting proliferative signaling and activating apoptotic machinery. The observed MAPK-mediated apoptosis mechanism provides novel insights for melanoma therapeutics, suggesting that combinatorial targeting of proteasomal and MAPK pathways may enhance treatment efficacy.
Keywords: Antitumor; Apoptosis effects; MG132; Melanoma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MG132 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia via Akt/FOXO3a/Bim pathway.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2024 Jan-Dec;43:9603271241303030. doi: 10.1177/09603271241303030. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39586583
-
Proteasome inhibitor MG132 induces thyroid cancer cell apoptosis by modulating the activity of transcription factor FOXO3a.Endocrine. 2017 Apr;56(1):98-108. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1256-y. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 28220348
-
Differential modulatory effects of GSK-3β and HDM2 on sorafenib-induced AIF nuclear translocation (programmed necrosis) in melanoma.Mol Cancer. 2011 Sep 19;10:115. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-115. Mol Cancer. 2011. Retraction in: Mol Cancer. 2021 Jun 15;20(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01378-8. PMID: 21929745 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Molecular hybridization design and synthesis of novel spirooxindole-based MDM2 inhibitors endowed with BCL2 signaling attenuation; a step towards the next generation p53 activators.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Dec;117:105427. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105427. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34794098
-
Oxyfadichalcone C inhibits melanoma A375 cell proliferation and metastasis via suppressing PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways.Life Sci. 2018 Aug 1;206:35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.05.032. Epub 2018 May 18. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29782872
Cited by
-
Nanoencapsulation of morin hydrate with BSA for sustained drug release in colorectal carcinoma cells: experimental and computational approach.Front Drug Deliv. 2025 Aug 13;5:1623317. doi: 10.3389/fddev.2025.1623317. eCollection 2025. Front Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 40837708 Free PMC article.
-
20-Hydroxyecdysone Modulates Bmp53-Mediated Apoptosis Regulation by Suppressing Mdm2-like-Dependent Ubiquitination in Silkworm, Bombyx mori.Insects. 2025 May 21;16(5):544. doi: 10.3390/insects16050544. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40429257 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

