EGCG Regulates the Effect of HDAC6 on Oxidative Stress of Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts Induced by Lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 40289388
- PMCID: PMC12034745
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.70198
EGCG Regulates the Effect of HDAC6 on Oxidative Stress of Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts Induced by Lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
Background: Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) has anti-inflammatory and antioxidative stress effects in periodontitis. However, the specific mechanisms involved remain unclear. Our study explored whether the mechanism by which EGCG on alleviates inflammation and oxidative stress in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts (hPDLCs) involves HDAC6.
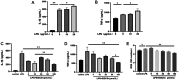
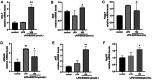
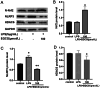
Methods: We treated hPDLCs with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and EGCG, and detected the resultant effects on cell proliferation by the CCK-8 method. Cells were divided into three groups: control, LPS, and EGCG + LPS. The expression of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the expression of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was detected using 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate. The expression of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6), p62, heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70), Kelch-like ECH-associating protein (Keap1), nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), and heme oxygenase-1(HO-1) mRNA was detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The protein expression of HDAC6, Nrf2, and nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) was detected by western blotting.
Results: At concentrations of less than 100 μmol/L, EGCG can promote cell proliferation and significantly inhibit the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β. Moreover, EGCG can activate the Nrf2 pathway and inhibit ROS production. Furthermore, EGCG inhibited the expression of HDAC6 and promoted the expression of p62 and Hsp70, indicating that the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of EGCG are closely related to HDAC6.
Conclusions: EGCG can regulate LPS-induced oxidative stress levels of hPDLCs through the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and reduce the expression of HDAC6-related factors. Therefore, HDAC6 may be a potential target for EGCG in the treatment of periodontal inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: HDAC6; Keap1/Nrf2/HO‐1; epigallocatechin gallate; periodontitis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
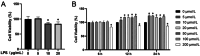
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

