Erythropoietin-Stimulated Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Chitosan Hydrogel Rescue BMSCs Fate by Targeting EGFR to Alleviate Inflammatory Bone Loss in Periodontitis
- PMID: 40289904
- PMCID: PMC12199399
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202500554
Erythropoietin-Stimulated Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Chitosan Hydrogel Rescue BMSCs Fate by Targeting EGFR to Alleviate Inflammatory Bone Loss in Periodontitis
Abstract
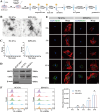
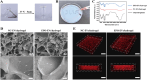
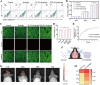
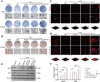
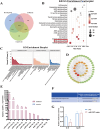
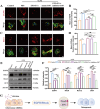
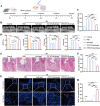
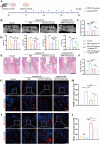
Loss of periodontal tissue due to persistent inflammation in periodontitis is a major cause of tooth loss in adults. Overcoming osteogenic inhibition in the inflammatory periodontal environment and restoring the regenerative capacity of endogenous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) remain critical challenges in current treatment approaches. Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) are key regulators of osteogenesis in recipient cells, yet the role of erythropoietin (EPO) in modifying macrophages and the function of their EVs in bone regeneration remain unclear. In this study, EVs from EPO-stimulated macrophages (EPO-EVs) are isolated, and they are encapsulated in a chitosan/β-sodium glycerophosphate/gelatin (CS/β-GP/gelatin) hydrogel to create a controlled-release EVs delivery system for localized periodontal environment. EPO-EVs restore the osteogenic function of mouse BMSCs (mBMSCs) and mitigate inflammatory bone loss in a periodontitis mouse model. Mechanistically, miR-5107-5p, significantly enriched in EPO-EVs, is delivered to mBMSCs, where it suppresses epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression and alleviates EGFR's inhibitory effect on RhoA. This process counteracts osteogenic inhibition in inflammatory settings through the EGFR/RhoA axis. Overall, EVs from EPO pretreated macrophages restore the osteogenic capacity of mBMSCs under inflammation by inhibiting EGFR expression, providing new insight into therapeutic mechanisms and offering a promising approach for future periodontitis treatment.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); erythropoietin; extracellular vesicles (EVs); microRNAs; periodontitis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from aspirin-treated macrophages promote osteochondral tissue regeneration.J Control Release. 2025 Sep 10;385:114052. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.114052. Epub 2025 Jul 17. J Control Release. 2025. PMID: 40683602
-
Lithium-doped calcium silicate scaffolds-activated M2-polarized macrophage-derived miR-145-5p-riched extracellular vesicles to enhance osteoimmunomodulation for accelerating bone regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Aug 25;23(1):586. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03679-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40855489
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate liver fibrosis via micro-7045-5p.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 May;480(5):2903-2921. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05152-4. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39516341
-
Skin regenerative potential of hydrogel matrices incorporated with stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles enriched with MicroRNAs: a systematic review.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jul;480(7):4035-4067. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05248-5. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40090986
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from Schwann cells to enhance bone and dental tissue regeneration: a literature review.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 11;23(1):502. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03585-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40646600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kinane D. F., Stathopoulou P. G., Papapanou P. N., Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17038. - PubMed
-
- Genco R. J., Sanz M., Periodontol. 2000 2020, 83, 7. - PubMed
-
- Marruganti C., Suvan J. E., D'Aiuto F., Periodontol. 2000 2023, 83, 7. - PubMed
-
- Sgolastra F., Petrucci A., Ciarrocchi I., Masci C., Spadaro A., J. Periodontol. Res. 2021, 56, 236. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
