Effects of 17,18-Epoxyeicosatetraenoic Acid and 19,20-Epoxydocosapentaenoic Acid Combined with Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor t-TUCB on Brown Adipogenesis and Mitochondrial Respiration
- PMID: 40289939
- PMCID: PMC11946110
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17060936
Effects of 17,18-Epoxyeicosatetraenoic Acid and 19,20-Epoxydocosapentaenoic Acid Combined with Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor t-TUCB on Brown Adipogenesis and Mitochondrial Respiration
Abstract
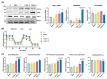
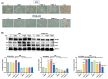
Background/Objectives: 17,18-epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (17,18-EEQ) and 19,20-epoxydocosapentaenoic acid (19,20-EDP) are bioactive metabolites produced from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), respectively, by CYP450s. These metabolites are unstable and quickly metabolized by auto-oxidation, esterification, β-oxidation, or hydrolysis by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). 17,18-EEQ or 19,20-EDP combined with a potent sEH inhibitor t-TUCB differentially activated brown adipose tissue in diet-induced obesity. In the current study, we investigated whether these n-3 epoxy fatty acids with t-TUCB directly promote brown adipocyte differentiation and their thermogenic capacities. Methods: Murine brown preadipocytes were treated with 17,18-EEQ or 19,20-EDP with t-TUCB during and post differentiation. Brown marker protein expression and mitochondrial respiration were measured. In addition, the activation of PPARγ and suppression of NFκB reporter by 17,18-EEQ or 19,20-EDP alone or with t-TUCB were assessed, and the roles of PPARγ were evaluated with PPARγ knockdown and GW9662. Results: 17,18-EEQ or 19,20-EDP with t-TUCB promoted brown adipogenesis and mitochondrial respiration and uncoupling. Moreover, with t-TUCB, both epoxides improved mitochondrial respiration, but only 17,18-EEQ with t-TUCB significantly increased mitochondrial uncoupling (and heat production) in the differentiated adipocytes. PPARγ may be required for the effects of epoxides on differentiation but not on the thermogenic function post differentiation. Conclusions: The results demonstrate that, with t-TUCB, 17,18-EEQ and 19,20-EDP promote brown adipogenesis and mitochondrial respiration and uncoupling. 17,18-EEQ also promotes thermogenesis in differentiated brown adipocytes. Together, the results suggest thermogenic potentials of tested n-3 epoxides, especially 17,18-EEQ with t-TUCB. Translational studies of these n-3 epoxides on human brown adipocyte differentiation and functions are warranted.
Keywords: 17,18-EEQ; 19,20-EDP; brown adipogenesis; n-3 epoxy fatty acid; soluble epoxide hydrolase; soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor t-TUCB; thermogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
C.M., K.S.S.L. and B.D.H are inventors on patents related to the use of sEH inhibitors owned by the University of California. B.D.H. is a co-inventor on a patent on the use of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors to treat diabetic nephropathy owned by the University of California. All other authors have nothing to disclose. B.D.H. is the founder, C.S.O. and part-owner of Eicosis, a small company advancing sEH inhibition for pharmacological applications.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Differential Effects of 17,18-EEQ and 19,20-EDP Combined with Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor t-TUCB on Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 31;22(15):8267. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158267. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361032 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase modulates inflammation and autophagy in obese adipose tissue and liver: role for omega-3 epoxides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 13;112(2):536-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1422590112. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25550510 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition by t-TUCB Promotes Brown Adipogenesis and Reduces Serum Triglycerides in Diet-Induced Obesity.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 24;21(19):7039. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197039. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32987880 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin interacts with PPARγ agonists to promote bovine adipocyte differentiation.Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2024 Jul;88:106848. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2024.106848. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38574690 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO The World Health Organization Obesity. [(accessed on 7 December 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1.
-
- CDC The US Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Adult Obesity Prevalence Maps. [(accessed on 7 December 2024)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data-and-statistics/adult-obesity-prevalence....
-
- CDC The US Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Consequences of Obesity. [(accessed on 7 December 2024)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basics/consequences.html.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

