Effects of 12-Week Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Education on Depressive Symptoms Among Depressed Patients with Breast Cancer Undergoing Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40289959
- PMCID: PMC11944683
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17060957
Effects of 12-Week Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Education on Depressive Symptoms Among Depressed Patients with Breast Cancer Undergoing Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
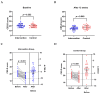
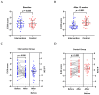
Background: Depressive symptoms (DepS) are prevalent among patients with breast cancer. Offering an anti-inflammatory diet is a promising strategy for DepS management, but it is costly and difficult to scale up. Instead, anti-inflammatory dietary education is cost-effective and may be more conducive to the promotion of an anti-inflammatory diet strategy. Methods: A prospective, assessor-blinded, two-arm randomized controlled trial was designed to determine the effects of 12-week anti-inflammatory dietary education on DepS in breast cancer patients with depression. Adult female patients with depression and receiving adjuvant chemotherapy were recruited. Participants in the intervention group received anti-inflammatory dietary education, while the control group received routine nursing care. Outcomes included the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) score, energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index (E-DII), plasma inflammatory biomarkers, and quality of life (QoL), which were all assessed at baseline and after a 12-week follow-up. The robustness of the estimates was investigated through sensitivity analyses. A post hoc power analysis was conducted to establish the observed effect sizes for the primary outcomes. Results: A total of 88.6% (62/70) of the participants completed the entire 12-week follow-up. No statistically significant between-group differences were found in the baseline characteristics, including sociodemographic factors, disease-related characteristics, and lifestyle factors. After the intervention, both the CES-D score (p = 0.040) and E-DII (p < 0.001) in the intervention group were significantly lower than in the control group, while the QoL was significantly increased (p < 0.001). Compared with the baseline, the tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (p = 0.002) and C-reactive protein (CRP) (p = 0.045) levels were significantly lower in the intervention group but not in the control group. Conclusions: Anti-inflammatory dietary education may improve DepS and QoL in breast cancer patients with depression and undergoing chemotherapy by regulating inflammation. Given its acceptability and practicality, this strategy may be incorporated into routine cancer care.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory diet; breast cancer; depressive symptoms; education; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Javan Biparva A., Raoofi S., Rafiei S., Masoumi M., Doustmehraban M., Bagheribayati F., Vaziri Shahrebabak E.S., Noorani Mejareh Z., Khani S., Abdollahi B., et al. Global depression in breast cancer patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2023;18:e0287372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287372. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

