Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Promotes Oligodendrocyte Maturation and Remyelination by Down-regulating the Interleukin-17A/Notch1 Signaling Pathway in Mice with Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 40290135
- PMCID: PMC12022504
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0676
Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Promotes Oligodendrocyte Maturation and Remyelination by Down-regulating the Interleukin-17A/Notch1 Signaling Pathway in Mice with Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
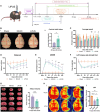
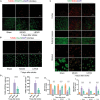
Increasing evidence indicates that oligodendrocyte (OL) numbers and myelin as a dynamic cellular compartment perform a key role in the maintenance of neuronal function. Inhibiting white matter (WM) demyelination or promoting remyelination has garnered interest for its potential therapeutic strategy against ischemic stroke. Our previous work has shown that low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) could improve stroke recovery. However, it is unclear whether LIPUS can maintain WM integrity early after stroke or promote late WM repair. This study evaluated the efficacy of LIPUS on WM repair and long-term neurologic recovery after stroke. Male adult C57BL/6 mice underwent a focal cerebral ischemia model and were randomized to receive ultrasound stimulation (30 min once daily for 14 days). The effect of LIPUS on sensorimotor function was assessed by modified neurological severity score, rotarod test, grip strength test, and gait analysis up to 28 days after stroke. We found that ischemic stroke-induced WM damage was severe on day 7 and partially recovered on day 28. LIPUS prevented neuronal and oligodendrocyte progenitor cell (OPC) death during the acute phase of stroke (d7), protected WM integrity, and reduced brain atrophy and tissue damage during the recovery phase (d28). To further confirm the effect of LIPUS on remyelination, we assessed the proliferation and differentiation of OPCs. We found that LIPUS did not increase the number of OPCs (PDGFRα+ or NG2+), but markedly increased the number of newly produced mature OLs (APC+) and myelin protein levels. Mechanistically, LIPUS may promote OL maturation and remyelination by down-regulating the interleukin-17A/Notch1 signaling pathway. In summary, LIPUS can protect OLs and neurons early after stroke and promote long-term WM repair and functional recovery. LIPUS will be a viable strategy for the treatment of ischemic stroke in the future.
Copyright © 2025 Jingjing Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Xiao Y, Czopka T. Myelination-independent functions of oligodendrocyte precursor cells in health and disease. Nat Neurosci. 2023;26(10):1663–1669. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

