The impact of age on the survival outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients after transarterial chemoembolization: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40290255
- PMCID: PMC12022578
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.41.4.11718
The impact of age on the survival outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients after transarterial chemoembolization: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background & objective: The efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in different populations of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients is still unclear. This meta-analysis explores the impact of TACE on survival outcomes in elderly versus younger patients with HCC, considering regional variations and heterogeneity among studies.
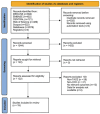
Methods: Nineteen studies involving 30,093 participants were systematically reviewed from January 1964 to January 2024. Data were pooled using random-effects models to calculate hazard ratios (HRs) and odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for overall survival and survival rates, respectively. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on age cut-offs and geographical regions to assess the effect of these variables on treatment outcomes.
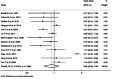
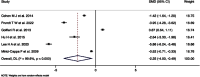
Results: Pooled HR for overall survival did not show a significant difference between elderly and younger patients (HR = 1.00; 95% CI: 0.98 to 1.02), with similar findings for survival rates (OR = 0.82; 95% CI: 0.46 to 1.45). Substantial heterogeneity was observed (I² = 78.0% for HR and 94.3% for OR), with notable regional differences indicating lower survival odds in European studies compared to Asian ones. No significant effect (OR = 0.95) was detected in prospective studies, while retrospective studies indicated a significant reduction in survival rates in elderly patients (OR = 0.35).
Conclusion: TACE appears to be equally effective in elderly and younger HCC patients. However, significant regional differences and study heterogeneity suggest the need for personalized treatment approaches. Further research is required to understand the underlying causes of these variations and to optimize TACE protocols.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Meta-Analysis; Older adults; Transarterial chemoembolization.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transarterial chemoembolization versus hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: a meta-analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Aug 10;9:4431-40. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S86629. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26309396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization improves survival outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019 Nov;45(11):2188-2196. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2019.06.031. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31256949
-
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) plus sorafenib versus TACE for intermediate or advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 19;9(6):e100305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100305. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24945380 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization combined with targeted therapy and immunotherapy versus with targeted monotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 3;103(18):e38037. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038037. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38701263 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of radiofrequency ablation in combination with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jun 28;19(24):3872-82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3872. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23840128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asafo-Agyei KO, Samant H. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Jun 12, Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 2024 Jan. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
