Establishing Sitafloxacin Epidemiological Cut-off Values (ECOFFs) for Clinical Bacterial Isolates
- PMID: 40290404
- PMCID: PMC12034273
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S501783
Establishing Sitafloxacin Epidemiological Cut-off Values (ECOFFs) for Clinical Bacterial Isolates
Abstract
Objective: To establish the epidemiological cut-off values (ECOFFs) of sitafloxacin against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
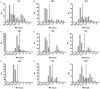
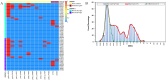
Methods: We collected 2264 clinical isolates from five different labs located in four cities in China. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) and inhibition zone diameters of sitafloxacin for all isolates were determined by using the broth microdilution method (BMD) and the disk diffusion method according to European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) guidelines. MIC ECOFFs were determined using ECOFFinder software, with the 99% calculated ECOFF selected as the initial value. Zone diameter ECOFFs were determined via the visual estimation method. Whole-genome sequencing was performed on E. coli strains exhibiting overlapping MICs between wild-type (WT) and non-wild-type (NWT) groups to analyze resistance mechanisms.
Results: Sitafloxacin MICs ranged from 0.002 to 64 mg/L, while inhibition zone diameters ranged from 6 to 45 mm across the nine species. MIC ECOFFs were determined as 0.032, 0.064, 0.125, 0.5, 0.064, 0.125, 0.5, 0.25, and 0.125 mg/L for E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis (tentative ECOFF), P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, S. aureus, E. faecalis, E. faecium, and S. pneumoniae, respectively. Except for S. pneumoniae, MICs of the other eight species showed a high correlation with zone diameters (|r| > 0.8, P < 0.0001). Consequently, the zone diameter ECOFFs were established as 26, 25, 24, 24, 25, 26, 21, and 22 for E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, S. aureus, E. faecalis, and E. faecium, respectively.
Conclusion: We established MIC and zone diameter ECOFFs for sitafloxacin against the nine species listed above. The MIC ECOFF for P. mirabilis was classified as tentative. For S. pneumoniae, the correlation between zone diameters and MICs was insufficient to establish a zone diameter ECOFF.
Keywords: BMD; ECOFF; MIC; disk diffusion; sitafloxacin; zone diameter.
© 2025 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Thiazole-pyrazoline hybrids as potential antimicrobial agent: synthesis, biological evaluation, molecular docking, DFT studies and POM analysis. J mol Struct. 2023;1282. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.135191 - DOI
-
- Okumura R, Hirata T, Onodera Y, et al. Dual-targeting properties of the 3-aminopyrrolidyl quinolones, DC-159a and sitafloxacin, against DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV: contribution to reducing in vitro emergence of quinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;62:98–104. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn136 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

