Advances in omics technologies for traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of metabolic bone diseases
- PMID: 40290428
- PMCID: PMC12021879
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1576286
Advances in omics technologies for traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of metabolic bone diseases
Abstract
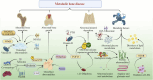
Metabolic bone disease (MBD), as one of the most severe metabolic disorders, remains a focal point and challenge in medical research. Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in preventing and treating MBD. However, the inherent complexity of TCM metabolites poses significant limitations in elucidating their mechanisms of action. The advancement of omics technologies, including metabolomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics, has greatly facilitated research on MBD. These approaches enable the identification of potential biomarkers and the exploration of metabolic pathways and mechanisms underlying TCM interventions for MBD. Evidence indicates that TCM monomers, single botanical drugs, and herbal formulations are effective, safe, and well-tolerated in MBD prevention and treatment. This review summarizes recent applications and key findings of transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics in studying the mechanisms of TCM interventions for MBD. It highlights the role of omics technologies in uncovering relevant metabolites and pathways under TCM treatment, providing valuable insights and clinical references for TCM-based strategies in managing MBD.
Keywords: metabolic bone disease; metabolomics; proteomics; traditional Chinese medicine (TCM); transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2025 Cai, Jiang, Zhao and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrating Multi-omics Technologies with Traditional Chinese Medicine to Enhance Cancer Research and Treatment.QJM. 2025 Apr 29:hcaf103. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcaf103. Online ahead of print. QJM. 2025. PMID: 40300104
-
Exploiting omic-based approaches to decipher Traditional Chinese Medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 3):118936. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118936. Epub 2024 Oct 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39413937 Review.
-
Clinical Applications of Omics Technologies on ZHENG Differentiation Research in Traditional Chinese Medicine.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:989618. doi: 10.1155/2013/989618. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23853666 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the "gene-protein-metabolite" network of coronary heart disease with phlegm and blood stasis syndrome by integrated multi-omics strategy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 29;13:1022627. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1022627. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36523490 Free PMC article.
-
Application of multi-omics in the study of traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 6;15:1431862. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1431862. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39309011 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baptista A. L., Padilha K., Malagrino P. A., Venturini G., Zeri A. C., Dos Reis L. M., et al. (2020). Potential biomarkers of the turnover, mineralization, and volume classification: results using NMR metabolomics in hemodialysis patients. JBMR plus 4 (7), e10372. 10.1002/jbm4.10372 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bian Q., Huang J. H., Yang Z., Ning Y., Zhao Y. J., Wang Y. J., et al. (2011). Effects of active ingredients in three kidneytonifying Chinese herbal drugs on gene expression profile of bone marrow stromal cells from a rat model of corticosteroneinduced osteoporosis. J. Chin. Integr. Med. 9 (02), 179–185. 10.3736/jcim20110211 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

