Smart materials strategy for vascular challenges targeting in-stent restenosis: a critical review
- PMID: 40290450
- PMCID: PMC12034381
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbaf020
Smart materials strategy for vascular challenges targeting in-stent restenosis: a critical review
Abstract
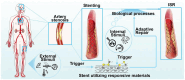
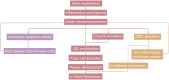
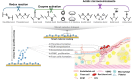
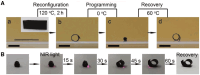
In-stent restenosis (ISR) presents a major challenge in vascular disease management, often leading to complications and repeated interventions. This review article explores the potential of existing smart materials strategies in addressing ISR, emphasizing advancements in materials science and biomedical engineering. We focus on innovative solutions such as bioactive coatings and responsive polymers that offer targeted responses to ISR-related internal and external triggers. These smart materials can dynamically adapt to the physiological conditions within blood vessels, responding in real time to various stimuli such as pH, oxidative stress and temperature. Moreover, we discuss preclinical progress and translational challenges associated with these materials as they move toward clinical applications. The review highlights the importance of controlled drug release and the need for materials that can degrade appropriately to minimize adverse effects. This work aims to identify critical research gaps and provide guidance to encourage interdisciplinary efforts to advance the development of smart stent technologies. Ultimately, the goal is to improve patient outcomes in vascular interventions by leveraging the capabilities of intelligent biomaterials to enhance ISR management and ensure better long-term efficacy and safety in-stent applications.
Keywords: in-stent restenosis; smart materials; targeted responses; triggers.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release from Smart Polymers.J Funct Biomater. 2019 Jul 31;10(3):34. doi: 10.3390/jfb10030034. J Funct Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31370252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the 4D printing linked bio-smart materials in dentistry: a concise overview.Front Dent Med. 2025 Apr 16;6:1558382. doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2025.1558382. eCollection 2025. Front Dent Med. 2025. PMID: 40309261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface Engineering of Bioactive Coatings for Improved Stent Hemocompatibility: A Comprehensive Review.Materials (Basel). 2023 Oct 29;16(21):6940. doi: 10.3390/ma16216940. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37959540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rationale and study design of the CardioGene Study: genomics of in-stent restenosis.Pharmacogenomics. 2004 Oct;5(7):952-1004. doi: 10.1517/14622416.5.7.949. Pharmacogenomics. 2004. PMID: 15469413
-
Recurrent Drug-Eluting Stent In-Stent Restenosis: A State-of-the-Art Review of Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management.Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2020 Sep;21(9):1157-1163. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2020. PMID: 31959561 Review.
References
-
- Huo X, Ma G, Tong X, Zhang X, Pan Y, Nguyen TN, Yuan G, Han H, Chen W, Wei M, et al., Investigators A-A. Trial of endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke with large infarct. N Engl J Med 2023;388:1272–83. - PubMed
-
- Stahli BE, Varbella F, Linke A, Schwarz B, Felix SB, Seiffert M, Kesterke R, Nordbeck P, Witzenbichler B, Lang IM. et al., MULTISTARS AMI Investigators Timing of complete revascularization with multivessel PCI for myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 2023;389:1368–79. - PubMed
-
- Farber A, Menard MT, Conte MS, Kaufman JA, Powell RJ, Choudhry NK, Hamza TH, Assmann SF, Creager MA, Cziraky MJet al. Investigators B-C, BEST-CLI Investigators Surgery or endovascular therapy for chronic Limb-Threatening ischemia. N Engl J Med 2022;387:2305–16. - PubMed
-
- Reed GW, Rossi JE, Cannon CP. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 2017;389:197–210. - PubMed
-
- Wu H, Ye P, Chen Y, Li Y, Cai C, Lv P. The current state of endovascular intervention for critical limb ischemia. Vasc Investig Ther 2021;4:46–53.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

