A Systematic Review of Surgical Techniques for the Repair of Capitellar Fractures
- PMID: 40291218
- PMCID: PMC12034337
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81304
A Systematic Review of Surgical Techniques for the Repair of Capitellar Fractures
Abstract
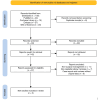
The rarity of capitellum fractures makes them a thorny problem in orthopedic practice, as fracture reduction and repair to restore joint function within a complex elbow joint are difficult. Properly treated, these fractures can avoid complications such as stiffness, instability, and posttraumatic arthritis. Several surgical techniques optimize patient outcomes, including open reduction with internal fixation using Herbert screws, buttress plating, and headless compression screws (HCS). The choice of technique, however, is determined by many factors, including fracture type, patient characteristics, and surgeon preference. This systematic review compares the clinical and functional outcomes of surgical techniques for capitellar fracture repair. Factors influencing the selection of surgical approach are also reviewed, including fracture complexity, patient demographics, and bone quality. To perform a systematic literature search, we followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and searched the major databases, including PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, and Web of Science. Search terms included "capitellar fracture", "elbow fracture", and "surgical fixation techniques". Clinical or biomechanical outcomes of capitellar fracture fixation using different surgical techniques were included, including fixation stability, range of motion, healing rates, and complication rates. In detail, three foundational studies were analyzed in depth, with the use of Herbert screws, Kirschner wires, and buttress plating. Clinical trials suggest that Herbert screws enable earlier mobilization and improved functional outcomes, particularly in younger patients with Type I fractures. Biomechanical studies, such as those using HCS with buttress plating, indicate enhanced stability, especially in osteoporotic bone conditions. Factors such as patient age, bone quality, and fracture pattern appear to influence the choice of surgical technique. Herbert screws provide effective fixation and support early mobilization, making them suitable for stable fractures in healthier patients. However, in cases of osteoporotic or complex fractures, augmented techniques, such as buttress plating, may be more appropriate to improve stability and reduce the risk of fixation failure. The selection of surgical techniques for capitellar fractures should take into account patient-specific factors to optimize clinical outcomes, and this review emphasizes the need for a tailored approach in selecting surgical techniques for capitellar fractures.
Keywords: capitellum; fixation; fracture; outcome studies; patient outcomes; surgical approach.
Copyright © 2025, Memon et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Buttress Plating on Biomechanical Stability of Coronal Shear Fractures of the Capitellum: A Cadaveric Study.J Hand Surg Am. 2023 Jun;48(6):621.e1-621.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.12.007. Epub 2022 Feb 10. J Hand Surg Am. 2023. PMID: 35153076 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical outcomes of capitellar fractures with posterior comminution treated with Herbert screws combined with metacarpal locking plates.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Dec 4;24(1):937. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-07065-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 38044433 Free PMC article.
-
Open reduction and internal fixation of capitellar fractures with headless screws. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009 Mar 1;91 Suppl 2 Pt 1:38-49. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.H.01195. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009. PMID: 19255199
-
Evaluating Kirschner wire fixation versus titanium plating and screws for unstable phalangeal fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis of postoperative outcomes.J Hand Microsurg. 2024 Mar 18;16(3):100055. doi: 10.1016/j.jham.2024.100055. eCollection 2024 Aug. J Hand Microsurg. 2024. PMID: 39035864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fractures of capitellum: a review of 14 cases treated by open reduction and internal fixation with Herbert screws.Int Orthop. 2010 Aug;34(6):897-901. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0896-9. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Int Orthop. 2010. PMID: 19894049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Capitellum fractures - trauma - orthobullets. [ Nov; 2024 ]. 2023. https://www.orthobullets.com/trauma/1023/capitellum-fractures. https://www.orthobullets.com/trauma/1023/capitellum-fractures.
-
- Technique for internal fixation of capitellum and lateral trochlea fractures. Mighell MA, Harkins D, Klein D, Schneider S, Frankle M. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:699–704. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources