Inspired Spine Smart Universal Resource Identifier (SURI): An Adaptive AI Framework for Transforming Multilingual Speech Into Structured Medical Reports
- PMID: 40291306
- PMCID: PMC12029695
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81243
Inspired Spine Smart Universal Resource Identifier (SURI): An Adaptive AI Framework for Transforming Multilingual Speech Into Structured Medical Reports
Abstract
Medical documentation is a major part of delivering healthcare worldwide and is gaining more importance in developing countries as well. The global spread of multilingual communities in medical documentation poses unique challenges, particularly regarding maintaining accuracy and consistency across diverse languages. Inspired Spine Smart Universal Resource Identifier (SURI), an adaptive artificial intelligence (AI) framework, addresses these challenges by transforming multilingual speech into structured medical reports. Utilizing state-of-the-art automatic speech recognition (ASR) and natural language processing (NLP) technologies, SURI converts doctor-patient dialogues into detailed clinical documentation. This paper presents SURI's development, focusing on its multilingual capabilities, effective report generation, and continuous improvement through real-time feedback. Our evaluation indicates a 60% reduction in documentation errors and a 70% decrease in time spent on medical reporting compared to traditional methods. SURI not only provides a practical solution to a pressing issue in healthcare but also sets a benchmark for integrating AI into medical communication workflows.
Keywords: artificial intelligence in medicine; dictation software; language interpretation services; large language model(llm); multilingual; patient encounter.
Copyright © 2025, Zhan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

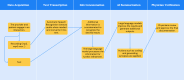
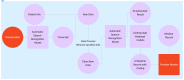


References
-
- High-precision medical speech recognition through synthetic data and semantic correction: UNITED-MEDASR. Banerjee S, Agarwal A, Ghosh P. https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.00055 Cor Uni. 2024
-
- Automatic recognition of spoken digits. Davis KH, Biddulph R, Balashek S. https://pubs.aip.org/asa/jasa/article-abstract/24/6/637/618458/Automatic... Jr Aco Soc Amr. 1952;24:637–642.
-
- Trainable grammars for speech recognition. Baker JK. https://pubs.aip.org/asa/jasa/article/65/S1/S132/739840/Trainable-gramma... IEEE. 1975;23:24–29.
-
- Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: the shared views of four research groups. Hinton G, Deng Li, Yu Dong, et al. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6296526 IEEE. 2012;29:82–97.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
