The Prognostic Value of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width-to-Albumin Ratio (RAR) in Predicting Mortality and Severity in Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40291314
- PMCID: PMC12032851
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81279
The Prognostic Value of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width-to-Albumin Ratio (RAR) in Predicting Mortality and Severity in Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Acute pancreatitis is a potentially life-threatening inflammatory condition with variable clinical presentations. Early risk stratification remains challenging despite existing scoring systems. The red blood cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio (RAR) has emerged as a potential prognostic biomarker in inflammatory conditions. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the association between admission RAR and outcomes in acute pancreatitis. We conducted a comprehensive literature search and identified five retrospective studies meeting the inclusion criteria. Meta-analysis was performed to assess the relationship between RAR and mortality as well as disease severity in acute pancreatitis patients. Pooled analysis demonstrated that elevated RAR was significantly associated with increased mortality risk (risk ratio (RR): 2.11, 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 1.35-3.30) with moderate heterogeneity (I²: 46%). When comparing disease severity, mean RAR values were significantly lower in mild acute pancreatitis compared to severe cases (mean difference (MD): -1.78, 95% CI: -2.09 to -1.46), also with moderate heterogeneity (I²: 44%). This meta-analysis suggests that RAR, a simple and cost-effective biomarker available from routine blood tests, may serve as a valuable prognostic indicator for mortality and severity in acute pancreatitis. Despite having comparatively lower discriminative ability than conventional scoring systems, RAR offers advantages in terms of rapid assessment and cost efficiency. However, limitations include the small number of included studies, their retrospective nature, and heterogeneity in study settings. Further prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; biomarker; mortality; prognostic; red blood cell distribution width albumin ratio.
Copyright © 2025, Hussaini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
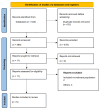
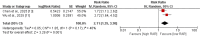
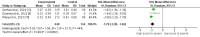
References
-
- New insights into acute pancreatitis. Lee PJ, Papachristou GI. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:479–496. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
