Effective adsorptive removal of triclosan from water using bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads
- PMID: 40291372
- PMCID: PMC12022511
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1547169
Effective adsorptive removal of triclosan from water using bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads
Abstract
Introduction: Triclosan is a common antibacterial drug identified as a major contaminant in South African waters, notably in Gauteng and KwaZulu Natal provinces. This contaminant comes from personal care products and pharmaceuticals. It has been frequently detected in local streams and wastewater treatment plants, posing a threat to aquatic ecosystems and human health. Studies have emphasised the necessity of addressing the presence of triclosan in water bodies to lessen its harmful impacts on the environment.
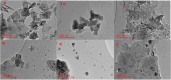
Methods: In this study, NaAlg/MnSx bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads incorporated with different amounts of MnS NPs (0.02-0.2 g) were synthesised via the ionic gelation method and employed as an adsorbent for the removal of triclosan from aqueous solutions. The surface charge, morphology, thermal stability, crystallinity, and functional groups of NaAlg/MnS bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads were characterised by SEM equipped with EDX, TEM, Thermogravimetric analysis, FTIR, XRD, and zeta sizer (mV).
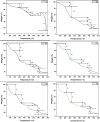
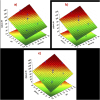
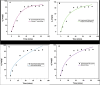
Results and discussions: The experimental results demonstrated that incorporating 0.02-0.2 g of MnS NPs in the bio-nanocomposite hydrogels led to enhanced mechanical structure, porosity, and swelling ability for the adsorption of triclosan compared to pristine NaAlg hydrogel. The response surface methodology was used to optimise the experimental parameters affecting the batch adsorption of triclosan onto the surface of the adsorbent. Basic pH conditions were suitable for removing triclosan in aqueous solutions via hydrogen bonding with the carboxyl functional groups of the bio-nanocomposite beads. The pseudo-second order, Freundlich, and Sips models better explained the adsorption kinetics and equilibrium isotherm data. The maximum adsorption capacity estimated using the Langmuir isotherm model was 132 mg/g. The thermodynamic parameters (enthalpy (∆H) and entropy (∆S)) were found to be 44.042 kJ/mol and 207.018 J/Kmol, respectively, which means the reaction is endothermic and increases randomisation at the solid/liquid interface. The Gibbs free energy (∆G) was negative throughout the studied temperature range, indicating that the adsorption process was spontaneously and energetically favoured.
Keywords: Triclosan; adsorption removal efficiency; bio-nanocomposite hydrogels; central composite design; manganese sulphide; sodium alginate.
Copyright © 2025 Mollo, Mnguni, Boikanyo, Nomngongo and Ramontja.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Abasalizadeh F., Moghaddam S. V., Alizadeh E., Akbari E., Kashani E., Fazljou S. M. B., et al. (2020). Alginate-based hydrogels as drug delivery vehicles in cancer treatment and their applications in wound dressing and 3D bioprinting. J. Biol. Eng. 14, 8–22. 10.1186/s13036-020-0227-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abin-Bazaine A., Trujillo A. C., Olmos-Marquez M. (2022). Adsorption isotherms: enlightenment of the phenomenon of adsorption. Wastewater Treat. 19, 1–5. 10.5772/intechopen.104260 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

