Neurophobia among students and interns at the Abidjan Faculty of Medicine (Côte d'Ivoire)
- PMID: 40291452
- PMCID: PMC12023870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ensci.2025.100566
Neurophobia among students and interns at the Abidjan Faculty of Medicine (Côte d'Ivoire)
Abstract
Introduction: As defined by Jozefowicz in 1994, neurophobia is the fear of neuroscience and clinical neurology. We carried out this study, the first on neurophobia in the Ivory Coast, in order to assess its prevalence among medical students and interns in the Ivorian environment, to identify the factors involved and to propose solutions.
Methodology: This was a prospective cross-sectional study carried out during the 2022-2023 academic year at the Abidjan UFR of Medical Sciences. The study population consisted of all students in years 3ème to 6ème and hospital interns. The Schon questionnaire, transcribed using google form software, was sent to students using the "wathsapp" social network.
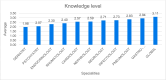
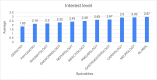
Result: We obtained 284 responses, i.e. 23 % of all respondents (n = 1228). The sex ratio was 1.65 in favour of men. The subjects considered that they had a level of competence in neurology higher than 6 of the nine specialities selected. These were nephrology, cardiology, rheumatology, endocrinology, psychiatry and geriatrics. Neurology was considered more difficult than cardiology, endocrinology, psychiatry and geriatrics. Subjects' level of knowledge in neurology was rated higher than in nephrology, cardiology, rheumatology, endocrinology, psychiatry and geriatrics. The subjects' level of interest in neurology was higher than in the other specialities. 27.46 % of subjects surveyed were neurophobic.
Conclusion: The impact of neurophobia remains harmful to public health, as it is a factor in the sub-optimal management of patients with neurological disorders.
Keywords: Abidjan; Medical students; Neurophobia.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Jozefowicz R.F. Neurophobia: the fear of neurology among medical students. Arch. Neurol. 1994;51:328–329. - PubMed
-
- Wasmine S. 2017. La Neurophobia chez les étudiants et les internes de la Faculté de Médecine et de Pharmacie de Rabat-à propos de 386 cas-. [UNIVERSITÉ MOHAMMED V - RABAT]: UNIVERSITÉ MOHAMMED V - RABAT.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

