IL-22 Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Epithelial Cell Apoptosis Associated with STAT3 Signalling
- PMID: 40291457
- PMCID: PMC12024478
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S496387
IL-22 Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Epithelial Cell Apoptosis Associated with STAT3 Signalling
Abstract
Purpose: Sepsis is a critical condition characterized by organ dysfunction due to an aberrant response to infection, which results in a life-threatening situation. The lung, which is the most vulnerable target organ, is often severely damaged during sepsis. Research has demonstrated that interleukin-22 (IL-22), which is secreted by various immunocytes, can mitigate inflammation-associated diseases. Nevertheless, the precise function of IL-22 in sepsis-induced acute lung injury (SALI) is still unclear. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of IL-22 in sepsis and explore the regulatory mechanisms involved.
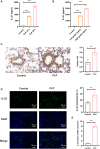
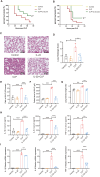
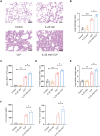
Methods: A mouse caecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model of sepsis was established, and the effect of IL-22 was investigated as indicated. Immunohistochemistry, qRT‒PCR, ELISA, immunofluorescence, TUNEL, Western blotting, and flow cytometry assays were applied to investigate the protective efficacy and involved pathways. Additionally, an in vitro model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced bronchial epithelial cell (BEAS-2B) apoptosis was established, and these cells were treated with or without recombinant IL-22 (rIL-22) to further evaluate the effect of IL-22 and the underlying mechanism.
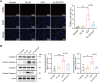
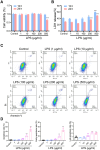
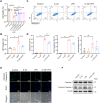
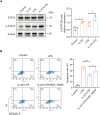
Results: The experimental results clearly confirmed that the levels of IL-22 were increased in the serum and lung tissue after CLP. The administration of rIL-22 was observed to increase the survival rate of septic mice. Notably, rIL-22 treatment resulted in decreased levels of proteins and a decreased cell number in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, as well as in a reduction in inflammatory cytokine release into the serum. Importantly, rIL-22 mitigated SALI by inhibiting lung cell apoptosis in septic mice. Furthermore, the results revealed that rIL-22 attenuated apoptosis of lung epithelial cells via the activation of the STAT3 signalling pathway.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that IL-22 alleviates lung epithelial cell apoptosis to protect mice against SALI in association with the STAT3 signalling pathway, highlighting the potential therapeutic value of IL-22 against sepsis.
Keywords: IL-22; STAT3; acute lung injury; apoptosis; sepsis.
© 2025 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work. This paper has been uploaded as a preprint to the Research Square website: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4198943/v1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Role and mechanism of ginsenoside Rg1 in ameliorating sepsis-induced acute lung injury based on PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP-induced alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jul;49(14):3837-3847. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240314.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39099357 Chinese.
-
Inhibition of gp130 alleviates LPS-induced lung injury by attenuating apoptosis and inflammation through JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway.Inflamm Res. 2023 Mar;72(3):493-507. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01686-9. Epub 2023 Jan 8. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 36617342
-
LncRNA H19 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by regulating the miR-107/TGFBR3 axis.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Sep 30;22(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02091-y. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36180862 Free PMC article.
-
Shenhuangdan decoction alleviates sepsis-induced lung injury through inhibition of GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt B):117047. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117047. Epub 2023 Aug 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37586442
-
Heat Shock Protein A12B Protects Vascular Endothelial Cells Against Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(1):156-168. doi: 10.1159/000477308. Epub 2017 May 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28535510
Cited by
-
Multi-Target Synergy Against Acute Lung Injury: Systems Pharmacology Decoding Dahuang-Huangqin Herb Pair's Therapeutic Mechanism.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 18;18:9413-9441. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S527378. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40703642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rehn M, Chew MS, Olkkola KT, Ingi Sigurðsson M, Yli‐Hankala A, Hylander Møller M. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock in adults 2021‐endorsement by the Scandinavian society of anaesthesiology and intensive care medicine. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2022;66(5):634–635. doi:10.1111/aas.14045 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

