Obstetric Nurses Perceptions About Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders: Photovoice Study
- PMID: 40291465
- PMCID: PMC12033399
- DOI: 10.1177/23333936241306206
Obstetric Nurses Perceptions About Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders: Photovoice Study
Abstract
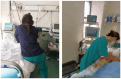
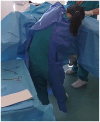
Obstetric nurses are at increased risk of work-related musculoskeletal disorders associated with equipment and materials, the parturient and the specific nature of their work. We used the photovoice method to identify obstetric nurses' perceptions of work-related musculoskeletal injuries involving 20 participants who worked in the delivery room. A total of 100 photographs were captured by participants and their narratives were obtained through 20 interviews. Analysis of the photographs, the nurses' descriptions of the photos, the researcher's field notes and the interviews, resulted in three semantic categories: perception of risk, perception of preventive measures and musculoskeletal symptoms, and one expressive category related to decision-making. Perceived risks for musculoskeletal injury were associated with workspaces, the precariousness of the equipment and materials, and the organization and nature of obstetrical nurses' work. The importance of preventive measures was recognized and reinforced by reports of transitory work-related musculoskeletal symptoms by 18 of 20 obstetric nurses participating in the study. The strategies perceived by the obstetric nurses as potentially effective for preventing musculoskeletal injury included improvements to the physical work environment and equipment, sensitization of the team to the problem, and developing biomechanical skills in situ through simulated exercises and peer support.
Keywords: Portugal; delivery rooms; obstetric nurses; perception; risk factors; work-related musculoskeletal disorders.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Risk perception of musculoskeletal injury among critical care nurses.Nurs Res. 2013 Jan-Feb;62(1):36-44. doi: 10.1097/NNR.0b013e31827334d6. Nurs Res. 2013. PMID: 23064312
-
Safe patient handling legislation and changes in programs, practices, perceptions, and experience of musculoskeletal disorders by hospital characteristics: A repeated cross-sectional survey study.Int J Nurs Stud. 2021 Jan;113:103791. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103791. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021. PMID: 33152606
-
Magnitude of work-related musculoskeletal disorders and its associated factors among Ethiopian nurses: a facility based cross-sectional study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jun 7;25(1):452. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07479-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38849729 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Interventions on Preventing Musculoskeletal Injuries Related to Nurses Work: Systematic Review.J Pers Med. 2023 Jan 20;13(2):185. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020185. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36836419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nurses' Perceptions of Their Practice Following a Redesign Initiative.Nurs Adm Q. 2020 Oct/Dec;44(4):E12-E24. doi: 10.1097/NAQ.0000000000000437. Nurs Adm Q. 2020. PMID: 32881808 Review.
References
-
- Bardin L. (2016). Content analysis. Edições; 70.
-
- Belotto M. (2018). Data analysis methods for qualitative research: Managing the challenges of coding, interrater reliability, and thematic analysis. The Qualitative Report, 23(11), 2622–2633. 10.46743/2160-3715/2018.3492 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

