Achieving single cell acoustic localisation with deactivation super resolution
- PMID: 40291471
- PMCID: PMC12021647
- DOI: 10.1038/s44384-025-00008-7
Achieving single cell acoustic localisation with deactivation super resolution
Abstract
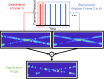
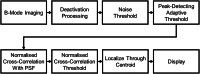
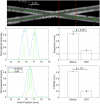
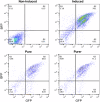
Photo-activated localization microscopy (PALM) has been a game-changer, breaking the diffraction limit in spatial resolution. This study presents the Deactivation Super Resolution (DSR) method, which utilises the deactivation of genetically encodable contrast agents, enabling us to super-resolve and pinpoint individual cells with ultrasound as they navigate through structures which cannot be resolved by conventional B-Mode imaging. DSR takes advantage of Gas Vesicles (GVs), which are air-filled sub-micron particles that have been expressed in genetically engineered bacterial and mammalian cells to produce acoustic contrast. Our experimental results show that DSR can distinguish sub-wavelength microstructures that standard B-mode ultrasound images fail to resolve by super-localising individual mammalian cells. This study provides a proof of concept for the potential of DSR to serve as a super-resolution ultrasound technique for individual cell localisation, opening new horizons in the field.
Keywords: Biological techniques; Engineering; Health care.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Achieving Single Cell Acoustic Localisation with Deactivation Super Resolution.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 24:2024.09.20.614052. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.20.614052. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: NPJ Acoust. 2025;1(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s44384-025-00008-7. PMID: 39386583 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Yan, J. et al. Transthoracic ultrasound localization microscopy of myocardial vasculature in patients. Nat. Biomed. Eng. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-024-01206-6. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
