Direct air capture of CO2 for solar fuel production in flow
- PMID: 40291483
- PMCID: PMC12021658
- DOI: 10.1038/s41560-025-01714-y
Direct air capture of CO2 for solar fuel production in flow
Abstract
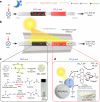
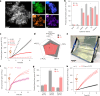
Direct air capture is an emerging technology to decrease atmospheric CO2 levels, but it is currently costly and the long-term consequences of CO2 storage are uncertain. An alternative approach is to utilize atmospheric CO2 on-site to produce value-added renewable fuels, but current CO2 utilization technologies predominantly require a concentrated CO2 feed or high temperature. Here we report a gas-phase dual-bed direct air carbon capture and utilization flow reactor that produces syngas (CO + H2) through on-site utilization of air-captured CO2 using light without requiring high temperature or pressure. The reactor consists of a bed of solid silica-amine adsorbent to capture aerobic CO2 and produce CO2-free air; concentrated light is used to release the captured CO2 and convert it to syngas over a bed of a silica/alumina-titania-cobalt bis(terpyridine) molecular-semiconductor photocatalyst. We use the oxidation of depolymerized poly(ethylene terephthalate) plastics as the counter-reaction. We envision this technology to operate in a diurnal fashion where CO2 is captured during night-time and converted to syngas under concentrated sunlight during the day.
Keywords: Carbon capture and storage; Photocatalysis; Solar fuels.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsA patent application covering integrated direct air capture and utilization into solar fuels has been submitted on behalf of the University of Cambridge via its technology transfer office, Cambridge Enterprise with co-inventors S. Kar and E.R. (application no. GB2408950.0). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- McQueen, N. et al. A review of direct air capture (DAC): scaling up commercial technologies and innovating for the future. Prog. Energy3, 032001 (2021). - DOI
-
- Erans, M. et al. Direct air capture: process technology, techno-economic and socio-political challenges. Energy Environ. Sci.15, 1360–1405 (2022). - DOI
-
- Chauvy, R. & Dubois, L. Life cycle and techno-economic assessments of direct air capture processes: an integrated review. Int. J. Energy Res.46, 10320–10344 (2022). - DOI
-
- Bui, M. et al. Carbon capture and storage (CCS): the way forward. Energy Environ. Sci.11, 1062–1176 (2018). - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
