Modulation of anti-tumour immunity by XPO1 inhibitors
- PMID: 40291981
- PMCID: PMC12022495
- DOI: 10.37349/etat.2025.1002310
Modulation of anti-tumour immunity by XPO1 inhibitors
Abstract
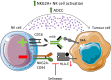
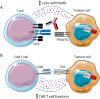
Exportin-1 (XPO1) is a nuclear export protein that, when overexpressed, can facilitate cancer cell proliferation and survival and is frequently overexpressed or mutated in cancer patients. As such, selective inhibitors of XPO1 (XPO1i) function have been developed to inhibit cancer cell proliferation and induce apoptosis. This review outlines the evidence for the immunomodulatory properties of XPO1 inhibition and discusses the potential for combining and sequencing XPO1i with immunotherapy to improve the treatment of patients with cancer. Selinexor is a first-in-class XPO1i that is FDA-approved for the treatment of patients with relapsed and refractory (RR) multiple myeloma and RR diffuse large B cell lymphoma. In addition to the cancer cell intrinsic pro-apoptotic activity, increasing evidence suggests that XPO1 inhibition has immunomodulatory properties. In this review, we describe how XPO1i can lead to a skewing of macrophage polarisation, inhibition of neutrophil extracellular traps, modulation of immune checkpoint expression, blockade of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and sensitisation of cancer cells to T cell and NK (natural killer) cell immunosurveillance. As such, there is an opportunity for selinexor to enhance immunotherapy efficacy and thus a need for clinical trials assessing selinexor in combination with immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, direct targeting monoclonal antibodies, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells and cereblon E3 ligase modulators (CELMoDs).
Keywords: ADCC; CAR-NK; CAR-T; Exportin-1 (XPO1); immunotherapy; selinexor.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
TK and CJW are employees and stockholders of Karyopharm Therapeutics. All the other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
