Overview of detection methods of fetomaternal haemorrhage
- PMID: 40292007
- PMCID: PMC12021815
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1445757
Overview of detection methods of fetomaternal haemorrhage
Abstract
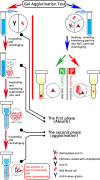
Fetomaternal haemorrhage is the same immunity that occurs when foetal and maternal blood are incompatible. It is critical to accurately quantify maternal haemorrhaging in order to prevent hemolytic disease in the infant. At this time, the rosette test and K-B test are the most frequently used techniques for detecting foetal red blood cells in the mother's blood. However, the sensitivity of the rosette test is low, and due to its complex operation and high subjectivity, the K-B test cannot be used as a routine clinical detection method. This review therefore focuses primarily on the clinical landscape and future prospects of methods for detecting fetomaternal haemorrhage. In a general sense, this may bring to light the most promising strategy and encourage the development of technology for fetomaternal haemorrhage in order to guarantee the early detection and prevention of hemolytic disease in newborns.
Keywords: detection method; fetal hemoglobin; fetomaternal haemorrhage (FMH); flow cytometry; hemolytic disease in newborns (HDN).
Copyright © 2025 Li, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

