Effects of Thymus daenensis Essential Oil-loaded chitosan Nanoparticles on BCR1 Gene Expression in Candida Parapsilosis
- PMID: 40292051
- PMCID: PMC12018755
- DOI: 10.32592/ARI.2024.79.5.973
Effects of Thymus daenensis Essential Oil-loaded chitosan Nanoparticles on BCR1 Gene Expression in Candida Parapsilosis
Abstract
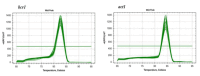
Candida parapsilosis is a non-albicans species with a high prevalence and potential for nosocomial infections. The BCR1 gene plays a critical role in regulating virulence factors in this species. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of Thymus daenensis essential oil encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles (TDNs) on the expression of the BCR1 gene in C. parapsilosis isolates from animal and human sources. Sixty C. parapsilosis isolates (30 from human and 30 from veterinary sources) were screened for the presence of the BCR1 gene via PCR. The TDNs were synthesized and characterized using various techniques. The isolates carrying the BCR1 gene were treated with TDNs to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The expression of the BCR1 gene after treatment with sub-MIC concentrations of TDNs was measured by real-time PCR and compared with the control group. The results were statistically analyzed. Five out of 60 isolates (8.33%) tested positive for the BCR1 gene. The physical properties of TDNs showed that they had a spherical shape, an average size of 92.3 nm, a polydispersity index of 0.129±0.03, a zeta potential of +48.3 mV, and an encapsulation efficiency of 88.6 ± 0.2%. The MIC range for TDNs in these isolates was 0.032-1 μg/ml. Treatment with TDNs significantly reduced the expression of the BCR1 gene in all five isolates compared with the control group (p=0.012). TDN has substantial potential for inhibiting the expression of the BCR1 gene, associated with virulence in C. parapsilosis. This may enhance the antifungal activity of TDN and reduce the risk of nosocomial infections caused by this species.
Keywords: BCR1; Gene Expression; Nanoparticles; Thymus Daenensis; Candida parapsilosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors certify that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could potentially influence the outcome of this research study. The study was not sponsored by any commercial entity. The authors assert that they have maintain complete independence in their research and conclusions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Investigation of the Effect of Farnesol on Biofilm Formation by Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis Complex Isolates].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2024 Jan;58(1):49-62. doi: 10.5578/mb.20249905r. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2024. PMID: 38263940 Turkish.
-
Characterization of biofilm formation and the role of BCR1 in clinical isolates of Candida parapsilosis.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Apr;13(4):438-51. doi: 10.1128/EC.00181-13. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 24297446 Free PMC article.
-
Triazole Evolution of Candida parapsilosis Results in Cross-Resistance to Other Antifungal Drugs, Influences Stress Responses, and Alters Virulence in an Antifungal Drug-Dependent Manner.mSphere. 2020 Oct 28;5(5):e00821-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00821-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 33115837 Free PMC article.
-
Candida and candidaemia. Susceptibility and epidemiology.Dan Med J. 2013 Nov;60(11):B4698. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24192246 Review.
-
Candida parapsilosis: from Genes to the Bedside.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019 Feb 27;32(2):e00111-18. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00111-18. Print 2019 Mar 20. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30814115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Selim AO, Abdel Salam MM, Abdallah Hassan RN, Mustafa GE, Abdelrahman Mahdy Z. The Effect of Some Nano Plant Extract on Bacteria Producing Biogenic Amines Isolated From Minced Meat. Iranian Journal of Veterinary Medicine. 2024;18(4):501–516.
-
- Hosseinabadi E, Garoussi MT, Khosravi AR, Gharagozloo F, Toosi BK, Moosakhani F. Prevalence of Prototheca and Fungal Contamination of Bulk Milk Tank of Industrial Dairy Cattle Herds in Iran. Iranian Journal of Veterinary Medicine. 2022;16(2):155–165.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
