Evaluation of the Impact of Selected Financial Indicators on Foreign Direct Investment in Bangladesh: A Nonlinear Modeling Approach
- PMID: 40292181
- PMCID: PMC12031603
- DOI: 10.1155/tswj/4406958
Evaluation of the Impact of Selected Financial Indicators on Foreign Direct Investment in Bangladesh: A Nonlinear Modeling Approach
Abstract
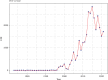
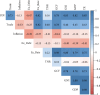
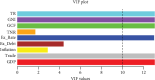
Background: Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a steadfast contributor to capital flows and plays an indispensable role in driving economic advancement and emerging as a pivotal avenue for financing growth in Bangladesh. Therefore, this study identifies the factors that influence FDI inflows in Bangladesh. Moreover, the authors explored the more appropriate model for predicting FDI by comparing the efficacy of other models' predictions. Methods: This study is based on secondary data over the period 1973 to 2021 and collected from the publicly accessible website of the World Bank. A generalized additive model (GAM) was implemented for describing the proper splines. The model's performance was assessed using the modified R-squared, the Bayesian information criterion (BIC), and the Akaike information criterion (AIC). Results: Findings depict a significant nonlinear relationship between Bangladesh's FDI and key economic indicators, including GDP, trade openness, external debt, gross capital formation, gross national income (GNI) and government rates of exchange, total reserves, and total natural resource rent. It is also observed that the GAM (R 2 = 0.987, AIC = 608.03, and BIC = 658.28) outperforms multiple linear regressions and polynomial regression in predicting FDI, emphasizing the superiority of GAM in capturing complex relationships and improving predictive accuracy. Conclusion: A nonlinear relationship is observed between FDI along with the covariates considered in this study. The authors believed that this study's findings would assist in taking efficient initiatives for FDI management and proactive economic indicator optimization to empower Bangladesh's economic resilience and foster sustainable growth. The analysis revealed that FDI and its related risk factors follow a nonlinear pattern. The study recommends using the GAM regression as a reliable method for predicting FDI in Bangladesh. The authors suggest that the findings can guide policymakers in developing strategies to increase FDI inflows, stimulate economic growth, and ensure sustainable economic development in Bangladesh.
Keywords: financial modeling; foreign direct investment (FDI); generalized additive model (GAM); nonlinear modeling.
Copyright © 2025 Md. Sifat Ar Salan et al. The Scientific World Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Relationships between total reserve and financial indicators of Bangladesh: Application of generalized additive model.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 7;18(4):e0284179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284179. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37027424 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring the impact of responsible factors on CO2 emission using generalized additive model (GAM).Heliyon. 2024 Feb 6;10(4):e25416. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25416. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38375290 Free PMC article.
-
The role of institutional quality in FDI inflows and carbon emission reduction: evidence from the global developing and belt road initiative countries.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Apr;29(20):30594-30621. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17958-6. Epub 2022 Jan 9. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35000154
-
Exploring the optimal threshold of FDI inflows for carbon-neutral growth in Africa.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Jan;31(2):2813-2835. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-31169-1. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38066263
-
Unlocking Africa's potential: The transformative power of foreign direct investment for sustainable development.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 28;10(5):e26507. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26507. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38468933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chowdhury T. S., Rahman M. H., Majumder S. C., Esquivias M. A. Significance of Technological Progress and Capital Formation to Expand Foreign Direct Investment in Bangladesh: Does Money Circulation Matter? Cogent Economics & Finance . 2023;11(2) doi: 10.1080/23322039.2023.2279351. - DOI
-
- Rahman M. C., Pede V. O., Balié J. Welfare Impact of Asymmetric Price Transmission on Rice Consumers in Bangladesh. Review of Development Economics . 2022;26(3):1600–1617. doi: 10.1111/rode.12882. - DOI
-
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and The Pacific. Asia-Pacific Trade and Investment Report 2021: Accelerating Climate-Smart Trade and Investment for Sustainable Development . United Nations; 2021.
-
- Kulkarni S., Hof A., Ambrósio G., et al. Investment Needs to Achieve SDGs: An Overview. PLOS Sustainability and Transformation . 2022;1(7) doi: 10.1371/journal.pstr.0000020.e0000020 - DOI
-
- Agba D. Z., Adewara S. O., Nwanji T. I., Yusuf M., Adzer K. T. Does Foreign Direct Investments Impact Agricultural Output in Nigeria? An Error Correction Modelling Approach. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development . 2018;9(4):67–77.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

