Evaluating the effect of crocin on contrast-induced nephropathy in rats
- PMID: 40292267
- PMCID: PMC12033014
- DOI: 10.22038/AJP.2024.24786
Evaluating the effect of crocin on contrast-induced nephropathy in rats
Abstract
Objective: Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) raises the risk of renal injury, but crocin, a saffron component, may improve kidney function. This study investigated crocin's protective effects against CIN in rats.
Materials and methods: Male Wistar rats were divided into eight groups: Sham, Control, Contrast medium (diatrizoate), Diatrizoate combined with crocin at 10, 20, or 40 mg/kg/day, Diatrizoate combined with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) at 125 mg/kg/day, and Crocin alone at 40 mg/kg/day. Water deprivation began on day 5 for 48 hr, except for the sham and crocin alone groups. Indomethacin and N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester were administered after 40 hr of dehydration. Rats were sacrificed on the eighth day, and blood and kidney samples were collected.
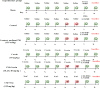
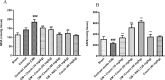
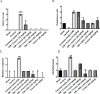
Results: Diatrizoate increased serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels, elevated malondialdehyde levels, and reduced glutathione in renal tissue. Crocin reversed these effects. Diatrizoate caused severe tubular necrosis, proteinaceous casts, medullary congestion, and interstitial edema in kidney tissue. Crocin (20 and 40 mg/kg) significantly reduced tubular necrosis, and doses of 10 and 40 mg/kg reduced interstitial edema. NAC significantly improved histopathological damage, biochemical factors, and oxidative stress. The crocin alone group showed no significant changes.
Conclusion: Diatrizoate induces nephrotoxicity by enhancing oxidative stress in rats, and crocin has a protective effect against it. Crocin mitigates both tissue and biochemical damage inflicted by diatrizoate.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Contrast medium; Diatrizoate; Indomethacin; L- NAME; Nephropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective effects of saffron (its active constituent, crocin) on nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015 Feb;34(2):127-34. doi: 10.1177/0960327114538989. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 24925368
-
Protective effect of crocin on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 Mar;19(3):337-43. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27114805 Free PMC article.
-
Crocin mediated amelioration of oxidative burden and inflammatory cascade suppresses diabetic nephropathy progression in diabetic rats.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Mar 25;284:90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29409856
-
Renoprotective effects of crocin against colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in a rat model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(2):151-156. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.72808.15843. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38234661 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of pathways involved in the protective effect of trans sodium crocetinate against contrast-induced nephropathy in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May;398(5):5373-5387. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03600-y. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39549062
Cited by
-
Effect of Crocus sativus L. (saffron) and Rosmarinus officinalis L. (rosemary) in hepatocellular carcinoma: A narrative review of current evidence and prospects.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(8):986-1003. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.84172.18204. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40584445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the efficacy of herbal supplements for managing obesity: A comprehensive review of global clinical trials.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(6):691-709. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.84150.18198. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40343290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herbal medicine approach to relieving dyspnea: A narrative review of efficacy and mechanisms.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(9):1140-1162. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.85518.18486. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40809176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alavizadeh SH, Hosseinzadeh H. Bioactivity assessment and toxicity of crocin: a comprehensive review. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;64:65–80. - PubMed
-
- Amin B, Hosseinzadeh H. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of Crocus sativus L.(saffron), Bioactive nutraceuticals and dietary supplements in neurological and brain disease. Elsevier; 2015. pp. 319–324.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
