Successful triple therapy for advanced synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma with metal stenting, photodynamic and comprehensive systemic therapies-shining light on hope: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 40292276
- PMCID: PMC12023257
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1580616
Successful triple therapy for advanced synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma with metal stenting, photodynamic and comprehensive systemic therapies-shining light on hope: a case report and literature review
Abstract
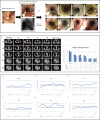
Synchronous multiple primary esophageal cancer (SMPEC) is a rare and aggressive condition often accompanied by obstructive dysphagia, significantly impacting patients' quality of life. Current treatments, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy, are limited in providing immediate symptom relief. This case report describes a 64-year-old female with SMPEC and metastases to thoracic lymph nodes, the lesser curvature of the stomach, and the right adrenal gland, presenting with severe dysphagia (score 4 on the Japanese Dysphagia Severity Scale). To rapidly alleviate symptoms, she underwent simultaneous metal stent implantation and photodynamic therapy (PDT). She started a liquid diet on the second day after treatment and resumed a normal diet one week later. Subsequently, she underwent systemic chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. By the third treatment cycle, primary and metastatic lesions significantly decreased, achieving a partial response (PR) with stable disease and progression-free survival (PFS) exceeded 12 months. This triple therapy approach-combining stent implantation, PDT, and systemic treatments-proved effective and safe for advanced SMPEC, not only providing immediate dysphagia relief and selective tumor destruction but also delaying disease progression and improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: chemotherapy; immunotherapy; metal stent implantation; photodynamic therapy; synchronous multiple primary esophageal cancer; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Zou, Yan, Li, Ma, Bai, Wang, Wang, Wang, Ma and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Morgan E, Soerjomataram I, Rumgay H, Coleman HG, Thrift AP, Vignat J, et al. The global landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in 2020 and projections to 2040: new estimates from GLOBOCAN 2020. Gastroenterology. (2022) 163:649–58.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.05.054 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

