Wound, pressure ulcer, and burn guidelines (2023)-4: Guidelines for the management of connective tissue disease/vasculitis-associated skin ulcers, third edition
- PMID: 40292847
- PMCID: PMC12149373
- DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.17703
Wound, pressure ulcer, and burn guidelines (2023)-4: Guidelines for the management of connective tissue disease/vasculitis-associated skin ulcers, third edition
Conflict of interest statement
According to Japanese Association of Medical Sciences (JAMS) Guidelines on COI Management in Medical Research (
Figures



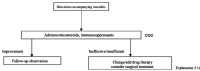


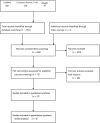

















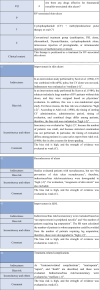



References
-
- Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, et al. 2012 revised international Chapel Hill consensus conference nomen‐clature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa F, Ikeda T, Ishiguro N, Uzuki M, Ozaki S, Katsuoka K. Guidelines for the management of vasculitis and vasculopathy (2016 revision). Jpn J Dermatol. 2017;127:299–415. - PubMed
-
- Wattiaux MJ, Kahn MF, Thevenet JP, Sauvezie B, Imbert JC. Vascular involvement in rheumatoid polyarthritis. Retrospective study of 37 cases of rheumatoid polyarthritis with vascular involvement and review of the literature. Ann Med Interne (Paris). 1987;138:566–587. - PubMed
-
- Salvarani C, Macchioni P, Mantovani W, Rossi F, Veneziani M, Boiardi L, et al. Extraarticular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis and HLA antigens in northern Italy. J Rheumatol. 1992;19:242–246. - PubMed
-
- Kaye O, Beckers CC, Paquet P, Arrese JE, Piérard GE, Malaise MG. The frequency of cutaneous vasculitis is not increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:253–257. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

