A Hybrid P&O and PV Characteristics Simulation Method for GMPPT in PV Systems Under Partial Shading Conditions
- PMID: 40293027
- PMCID: PMC11946778
- DOI: 10.3390/s25061908
A Hybrid P&O and PV Characteristics Simulation Method for GMPPT in PV Systems Under Partial Shading Conditions
Abstract
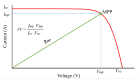
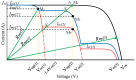
Under uniform operating conditions, the power-voltage (P-V) and current-voltage (I-V) curves of a photovoltaic (PV) system have only one maximum point, which facilitates the operation of maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithms. In practice, the PV systems often operate under heterogeneous environments due to partial shading conditions (PSCs). The P-V and I-V curves exhibit multiple extremes, and distinguishing between the global maximum power point (GMPP) and local maximum power point (LMPP) is a major challenge for algorithms aiming to improve performance and convergence speed. This paper presents a global maximum power point tracking (GMPPT) method based on simulating the behavior of the I-V curve of a PV system under the influence of PSCs. With only one initial parameter selected, the proposed solution quickly determines the LMPPs based on the characteristics of the PV type and the shading condition during operation. This work helps to limit the potential GMPP region to reduce the search time and improve efficiency by using a simple algorithm and a small tuning step size. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method provides superior MPPT performance and significantly reduces search time due to improved GMPP detection accuracy combined with small step sizes.
Keywords: GMPPT; P&O algorithm; open circuit voltage; partial shading conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
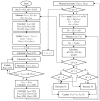
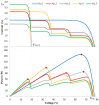

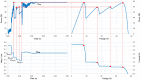
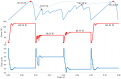

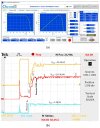
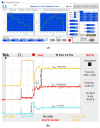
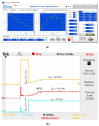

References
-
- Kumar M., Panda K., Rosas-Caro J., Valderrabano-Gonzalez A., Panda G. Comprehensive review of conventional and emerging maximum power point tracking algorithms for uniformly and partially shaded solar photovoltaic systems. IEEE Access. 2023;11:31778–31812. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3262502. - DOI
-
- Katche M., Makokha A., Zachary S., Adaramola M. A Comprehensive Review of Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Techniques Used in Solar PV Systems. Energies. 2023;16:2026. doi: 10.3390/en16052206. - DOI
-
- Bollipo R., Mikkili S., Bonthagorla P. Critical Review on PV MPPT Techniques: Classical, Intelligent and Optimisation. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020;14:1433–1452. doi: 10.1049/iet-rpg.2019.1163. - DOI
-
- Bollipo R., Mikkili S., Bonthagorla P. Hybrid, Optimal, Intelligent and Classical PV MPPT Techniques: A Review. Csee J. Power Energy Syst. 2021;7:9–33.
-
- Hassan A., Bass O., Masoum M. An improved genetic algorithm based fractional open circuit voltage mppt for solar pv systems. Energy Rep. 2023;9:1535–1548. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2022.12.088. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

