A State of the Science Review of Human Health Effects of the Michigan Polybrominated Biphenyl Contamination after Five Decades
- PMID: 40293296
- PMCID: PMC12161457
- DOI: 10.1289/EHP15012
A State of the Science Review of Human Health Effects of the Michigan Polybrominated Biphenyl Contamination after Five Decades
Abstract
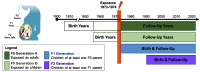
Background: The Michigan Polybrominated Biphenyl (PBB) Registry, followed since 1976, was created after a 1973 chemical manufacturing mistake. The flame retardant PBB was accidentally mixed into animal feed and distributed to Michigan farms for nearly a year, exposing farm residents and animal product consumers.
Objective: We synthesized knowledge to date on health effects of PBB exposure within the Michigan PBB Registry and describe research findings in the context of literature on other persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs).
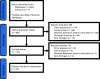
Methods: We reviewed literature published from 1973 to 2025 on human health effects of PBB following the Michigan contamination, using PubMed and Thompson Reuters (ISI) Web of Science databases. We excluded studies not in English; studies on exposures besides PBB; animal studies; reviews, abstracts, or letters to the editor; studies without a health outcome; and studies outside of Michigan or unrelated to the 1973 contamination. For each article, two researchers performed title and abstract screening, full article review, and data extraction.
Results: We included 79 publications out of 601 identified and screened. Early studies did not find many health outcomes associated with PBB, possibly because of methodological limitations. More recent studies on long-term and multigenerational impacts found an increased breast cancer risk, accelerated pubertal development and earlier menarche for girls exposed in utero, urogenital problems and slower pubertal development in boys exposed in utero, lower estrone 3-glucuronide and follicle-stimulating hormone among women exposed in childhood, and increased miscarriage risk among daughters of exposed women. Epigenetic and metabolomic research reported altered pathways related to estrogenic effects and immune function as well as the epigenetic alterations of spermatogenic cells.
Discussion: This unique community-academic partnership has produced insights into multigenerational consequences of EDC/POP exposures across the life course. The findings from this cohort underscore the broader relevance of critical windows of vulnerability, particularly during fetal development and childhood. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP15012.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mortality of individuals in a long-term cohort exposed to polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs).Environ Health. 2025 Jul 1;24(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12940-025-01192-5. Environ Health. 2025. PMID: 40598219 Free PMC article.
-
The epidemiologic evidence linking prenatal and postnatal exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals with male reproductive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Dec;23(1):104-125. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw036. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 27655588 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental exposure to indoor flame retardants and hypothalamic molecular signatures: Sex-dependent reprogramming of lipid homeostasis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 30;13:997304. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.997304. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36277707 Free PMC article.
-
Participation in environmental enhancement and conservation activities for health and well-being in adults: a review of quantitative and qualitative evidence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 21;2016(5):CD010351. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010351.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27207731 Free PMC article.
-
Regional cerebral blood flow single photon emission computed tomography for detection of Frontotemporal dementia in people with suspected dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 23;2015(6):CD010896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010896.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26102272 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

