Target Screening and Single Cell Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy and Hepatocarcinoma
- PMID: 40293350
- PMCID: PMC12128161
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70521
Target Screening and Single Cell Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy and Hepatocarcinoma
Abstract
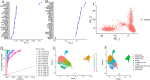
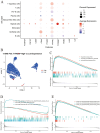
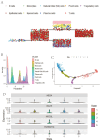
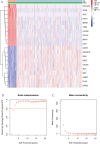
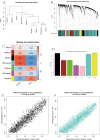
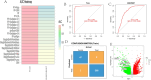
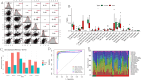
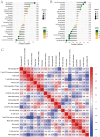
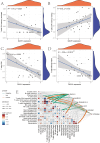
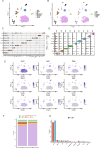
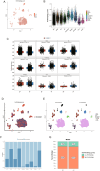
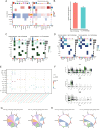
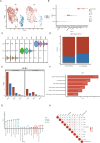
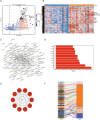
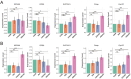
The association between liver cancer and diabetes has been a longstanding focus in medical research. Current evidence suggests that diabetes is an independent risk factor for the development of liver cancer. Diabetic retinopathy (DR), a prevalent neurovascular complication of diabetes, has yet to be fully characterised concerning liver cancer. Therefore, this study seeks to identify shared genes and pathways between liver cancer and DR to uncover potential therapeutic targets. Immune infiltration and cell communication in liver cancer were analysed using the GEO single-cell dataset GSM7494113. Single-cell RNA sequencing data from rat retinas were obtained from the GEO datasets GSE209872 and GSE160306. Ferritin phagocytosis-related genes were retrieved from the GeneCards database. The SeuratR package was employed for single-cell clustering analysis, while the CellChat package assessed differences in intercellular communication. Genes shared between DR and liver cancer were identified, and the DGIDB database was consulted to predict potential drug-gene interactions targeting membrane proteins involved in ferritin phagocytosis. Key ferritin phagocytosis (FRHG) genes were further validated using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). After annotating the single-cell data through dimensionality reduction and clustering, the expression of genes associated with membrane protein-related ferritinophagy was notably elevated in both HCC and DR samples. Based on the expression of ferritinophagy-related genes, the ferritin deposition score in Müller cells from the DR group was significantly higher than that in the control group. Cell communication analysis revealed that central hub genes associated with ferritinophagy, such as PSAP and MK, along with other signalling pathways, were significantly upregulated in the high Müller group compared to the low Müller group. In contrast, VEGF expression was enhanced in the low Müller group. Importantly, the machine learning model constructed using these key hub genes demonstrated high diagnostic efficacy for both HCC and DR. Finally, by simulating a hyperosmotic diabetic microenvironment, we confirmed in vitro that high glucose conditions significantly stimulate the expression of the shared key hub genes in both HCC and DR. The present study identified the connection between ferritinophagy-related subgroups of cells and key hub genes in both HCC and DR, providing new insights into DR-associated biomarkers and the shared pathological regulatory pathways with HCC. These findings further suggest potential therapeutic targets for both diseases.
Keywords: Müller cells; diabetic retinopathy; ferritin phagocytosis; liver cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrative analysis of PANoptosis-related genes in diabetic retinopathy: machine learning identification and experimental validation.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 4;15:1486251. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1486251. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39697326 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating single-cell RNA-Seq and bulk RNA-Seq data to explore the key role of fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 15;15(1):2077. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85506-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39814999 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of ferritinophagy-related genes and immune infiltration landscape in diabetic retinopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 14;14:1177488. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1177488. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37522124 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Molecular Complexity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Unveiling Novel Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets Through Advanced Bioinformatics Analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Aug;7(8):e2152. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2152. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 39118438 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Efferocytosis-Related Genes and Mechanisms in Diabetic Retinopathy.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jul;67(7):2785-2797. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01239-x. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39085562
References
-
- Kubo T., Yanagihara K., Nishimura Y., et al., “Antitumor Effect of Oleoyl‐siRNA Against Pancreatic Cancer Using a Portal Vein Infusion Liver‐Metastatic Mouse Model,” Molecular Pharmaceutics 21 (2024): 5115–5125. - PubMed
-
- Ho N. T., Abe S. K., Rahman M. S., et al., “Diabetes Is Associated With Increased Liver Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Adults: A Report From Asia Cohort Consortium,” International Journal of Cancer 155, no. 5 (2024): 854–870. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

